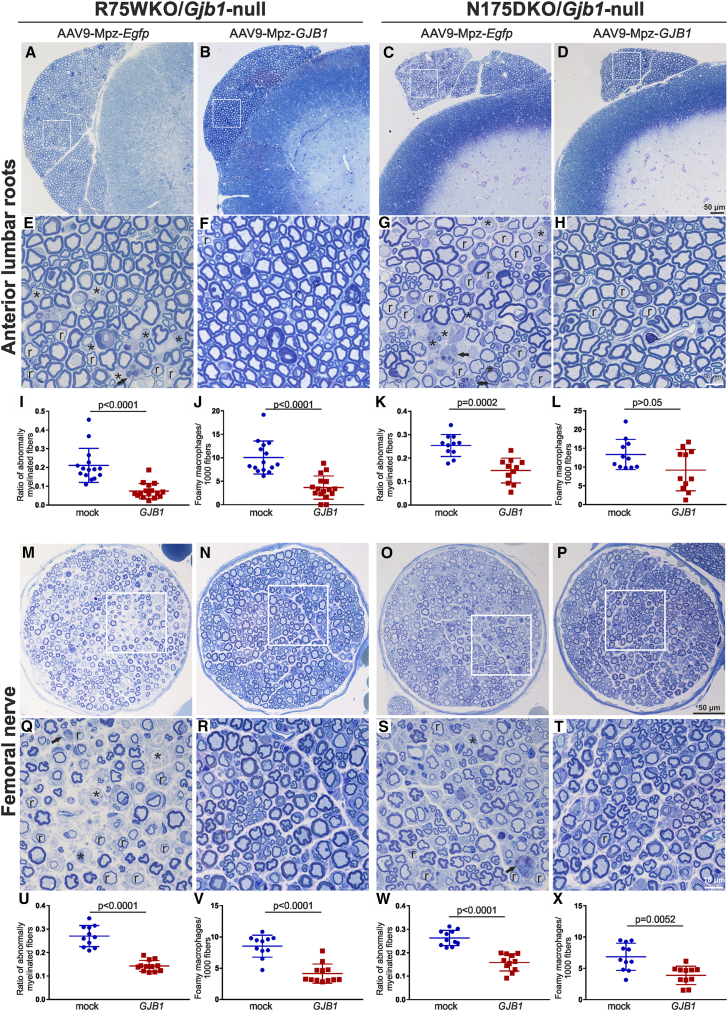
Figure 3.
Morphological analysis of anterior lumbar roots and femoral motor nerves of pre-onset-treated R75W/Gjb1-null and N175D/Gjb1-null mice at 8 months of age (6 months after treatment)
Representative images of semithin sections of R75W/Gjb1-null (A, B, E, and F) and N175D/Gjb1-null (C, D, G, and H) anterior motor lumbar spinal roots attached to the spinal cord, at low and higher magnification, as indicated. AAV9-Mpz.GJB1-injected mice show improved root myelination compared to mock-treated littermates with fewer demyelinated (∗) and remyelinated (r) fibers, as well as reduced numbers of foamy macrophages (arrows in E and G). Improved root pathology is confirmed by the morphometric analysis results, showing decreased ratios of abnormally myelinated fibers and reduced numbers of macrophages per 1,000 fibers in treated mice except for the macrophage reduction in N175D/Gjb1-null roots not reaching statistical significance (I–L). Semithin sections of femoral motor nerves of R75W/Gjb1-null (M, N, Q, and R) and N175D/Gjb1-null (O, P, S, and T) at lower and higher magnification as indicated, and corresponding morphometric analysis results (U–X) from mock- and full-vector-treated mice as indicated. AAV9-Mpz.GJB1-injected mice show improved myelination in femoral nerves compared to mock-treated littermates with fewer demyelinated and remyelinated fibers as well as reduction in the numbers of foamy macrophages, confirmed by quantification. Values represent mean±SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using the Mann-Whitney test.