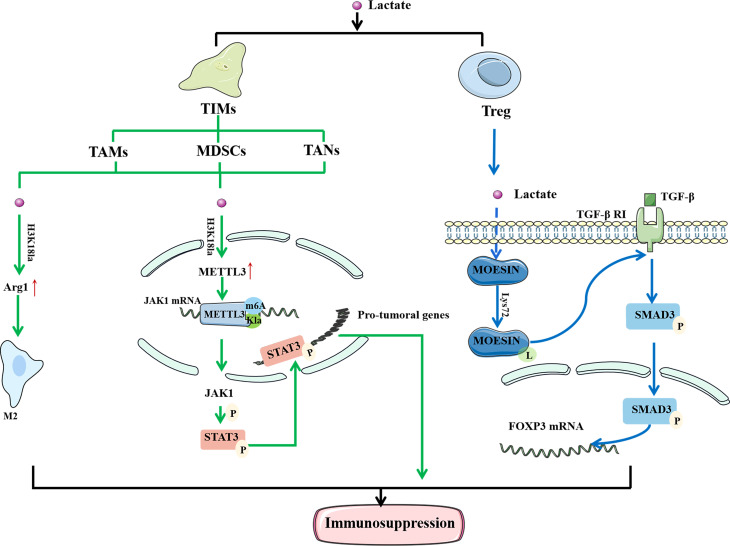
Figure 3.
Lactylation regulates the function of immune cells to mediate immunosuppression. In TAM, histone lactylation will lead to the up-regulation of M2 phenotypically related genes, thereby mediating the M2 polarization. In TIMs, histone lactylation promote the expression of METTL3, and METTL3 mediates the m6A modification of JAK1 mRNA. At the same time, there are also lactylation sites in METTL3 that allow it to bind to the target RNA. Moesin can reduce the expression of TGF-β receptor and inhibit the production of Treg cells to restore anti-tumor immunity. Lactate can inhibit the function of moesin by promoting Lys72 site lactylation to mediate the generation of Treg cells and promote the immune escape of tumor cells. In conclusion, lactylation is closely related to the immunosuppression of tumors. LPS, Lipopolysaccharide; IFN γ, Interferon-gamma; IL-4, interleukin-4; IL-13, interleukin-13; TAM, tumor-associated macrophages; TIM, tumor -infiltrating myeloid cells; Arg1, arginase 1; METTL3, methyltransferase-like 3; JAK1, Janus Kinase 1; M6A, N6-methyladenosine; TGF-β, transforming growth factor beta.