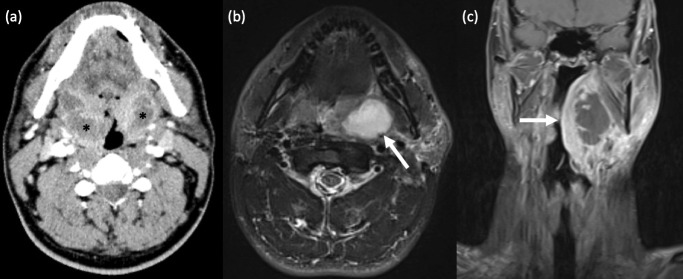
Figure 4.
Tonsillitis with peritonsillar abscess. (a) Bilateral peritonsillar abscesses. A 42-year old male had persistent parapharyngeal swelling following aspiration of only a right peritonsillar collection. Axial contrast-enhanced CT Neck revealed bilateral, peripherally enhancing, centrally hypodense peritonsillar collections, in keeping with abscesses, larger on the right. Unilateral peritonsillar abscess is more common. (b,c) Left peritonsillar abscess. (c) Axial T2-weighted STIR MRI shows a well-defined, left peritonsillar collection with homogenous, central hyperintensity. (d) Coronal T1-weighted, fat-suppressed, post-contrast MRI in the same patient demonstrates a left peritonsillar abscess with central non-enhancement and marked peripheral enhancement, and extension of diffuse inflammatory changes into the adjacent left parapharyngeal and submandibular spaces.