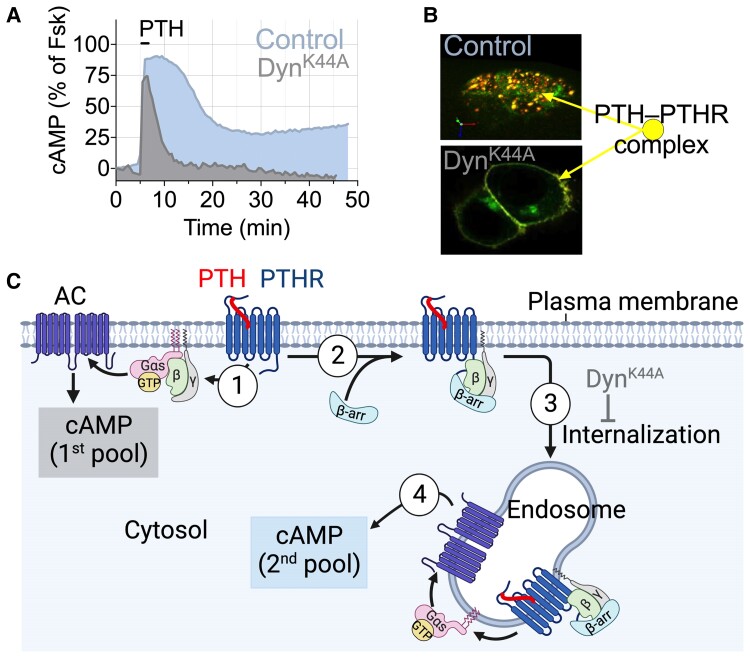
Figure 3.
Modes of PTH1R signaling via cAMP. (A) Time courses of cAMP production induced by PTH1-34 in single cell (here a mouse osteoblast) without (control) or with expression of the recombinant dominant-negative dynamin mutant (DynK44A) that blocks receptor internalization. (B) Confocal images representing a 3D view of HEK-293 cells expressing PTH1R N-terminally tagged with GFP (PTHRGFP) with TMR-labeled PTH1-34 (PTHTMR). In control cells, PTH1RGFP and PTHTMR colocalized (colored spots) in endosomes; in cells coexpressing Dyn-K44A, the ligand–receptor complex remains at the cell surface. (C) The 1st pool of cAMP production takes place at the cell membrane following PTH binding to PTH1R (step 1). This response is short-lived due to rapid receptor desensitization via PTHR phosphorylation by GPCR kinases, followed by recruitment of β-arrestins (β-arrs) (step 2) driving receptor internalization and its redistribution in early endosomes (step 3). PTH interacts tightly with PTH1R in a conformation-dependent fashion and induces the 2nd pool cAMP production from endosomes (step 4). Endosomal cAMP production is prolonged until endosomal acidification induces the release of PTH from the receptor. Created with BioRender.