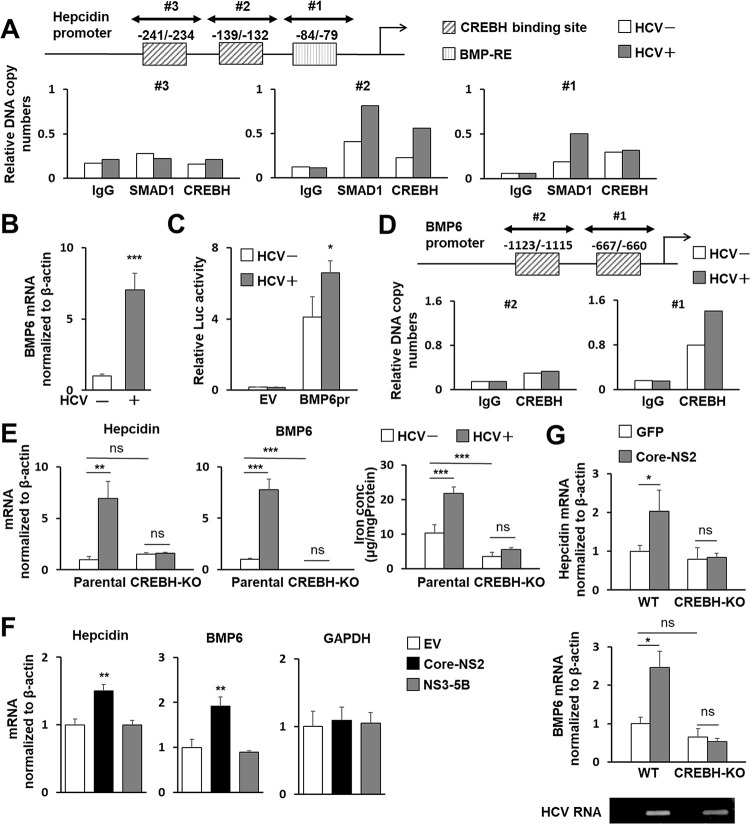
Fig 2. Role of CREBH in hepcidin and BMP6 expression induced by HCV infection or protein expression.
(A) Nuclear fractions from infected cells 3 dpi (MOI = 0.5) and cells without infection were used for ChIP assays. Protein-DNA complexes were immunoprecipitated with antibodies against either SMAD1 or CREBH or with rabbit IgG, analyzed by qPCR using three primer sets: Hepcidin pr ChIP set #1-#3. The sites potentially recognized by CREBH or BMP6 are indicated. (B) BMP6 mRNA in cells with and without HCV infection was analyzed using qRT-PCR. (C) BMP6 promoter reporter (BMP6pr) or basal reporter (EV; empty vector) was transfected into cells with HCV infection at 1 dpi and without infection. Firefly luciferase activities normalized by Renilla luciferase in cells at 2 days post-transfection (dpt) were determined. (D) ChIP assays and immunoprecipitations were performed as described in (A) with anti-CREBH antibody against or rabbit IgG. Precipitates were analyzed for qPCR using two primer sets: BMP6 pr ChIP set #1 and #2. The CREBH-binding sites are indicated. (E) CREBH-KO and parental Huh7.5.1 cells were cultured with or without HCV infection for 3 days, after which the mRNA of hepcidin (left) and BMP6 (middle) were quantified and the iron concentration (right) was measured by the Nitroso-PSAP. (F) Cells were transfected with a plasmid expressing Core-NS2 or NS3-5B or an EV. At 2 dpt, mRNAs of hepcidin, BMP6, and GAPDH were quantified. (G) Eight-week-old male WT and Creb3l3−/− mice were intravenously injected with AdV expressing Cre recombinase (AdEFNCre) together with AdV expressing either GFP (AdEFLNLGFP) or Core-NS2 (AdEFLNLHCVCore/NS2). At 5 dpi, total RNAs from liver tissues were extracted, followed by determining hepcidin and BMP6 mRNAs. Expression of HCV RNA was detected by RT-PCR. (B, E-G) Results represent the means with SD from three independent measurements. Student’s t test; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P <0.001.