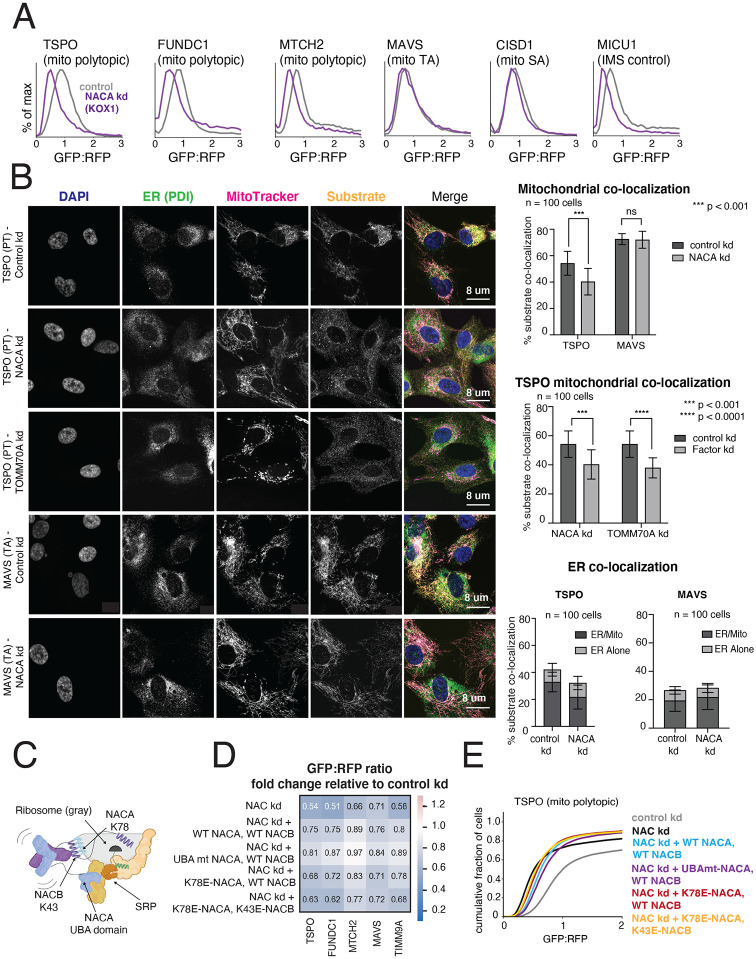
Figure 4. The NAC complex is required for the efficient delivery of polytopic α-helical proteins to the mitochondrial outer membrane.
(A) Integration of indicated GFP11-fused SA, TA, polytopic and IMS control reporters in K562 KOX1 CRISPRi cells constitutively expressing IMS GFP1-10 and either a sgRNA targeting NACα or a non-targeting sgRNA (control). (B) (Left) Changes in localization of endogenous TSPO (polytopic) and MAVS (TA) were assessed using immunostaining and confocal microscopy in RPE1 ZIM3 CRISPRi cells expressing sgRNAs targeting NACα, TOMM70 or a non-targeting control. Merge colors: Blue: DAPI, Green: ER, Yellow: Substrate, Magenta: MitoTracker. (Right) Quantification of endogenous substrates co-localized to MitoTracker (mitochondrial marker) and PDI (ER marker) were measured and plotted (see Methods for details). Quantification of substrates co-localized to the ER were split into i) percent co-localized to ER/MitoTracker overlapping regions and ii) percent co-localized to the rest of the ER (‘ER alone’) (see FIgure S6D). For more detailed substrate localization analysis across all conditions, see Figures S6C-F. Error bars show mean ± SD of 100 cells. Statistical significance was evaluated by multiple unpaired t-tests with the Holm-Sidak multiple test correction. ***, p < 0.001. ****, p < 0.0001. ns (non-significant), p > 0.05. (C) Model of a translating ribosome engaging NAC and SRP. NACα (blue) and NACβ (purple) interact with the ribosome (gray) through electrostatic interactions mediated by the indicated lysine residues (NACα K78 and NACβ K43). SRP is recruited to the ribosome through electrostatic interactions with the UBA domain of NACα (at residues D205 and N208), where it engages the substrate nascent chain (green) co-translationally. (D) The effects of ribosome-binding mutants of NACα and NACβ (K78E and K43E respectively) and a UBA-domain binding mutant of NACα (D205R + N208R) on integration of select GFP11-fused reporters in K562 KOX1 CRISPRi IMS GFP1-10 cells was tested using a similar strategy as in Figures 3E and 3G. Both members of the NAC complex were simultaneously depleted using CRISPRi and abilities of exogenous wild-type (WT) and mutant versions of NACα and NACβ to rescue reporter integration defects were assessed. Rescue constructs are in a cassette with a BFP translation marker. Data is represented as a heatmap colored by the effects of exogenous additions of NACα and NACβ (WT and mutant versions as indicated) on reporter integration in the mitochondria relative to the control condition (non-targeting sgRNA + BFP alone, as shown in Figures 3E and 3G). (E) Flow cytometry data for polytopic reporter TSPO across all conditions shown in (D) represented as a cdf plot. See Figures S6 and S7.