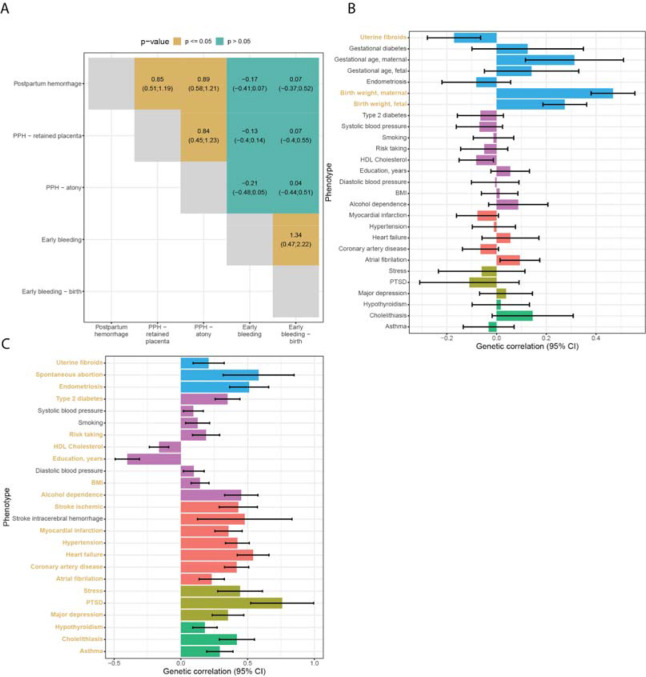
Figure 3.
(A) Cross-trait genetic correlation of all bleeding in pregnancy phenotypes (95% confidence interval). Postpartum hemorrhage and early bleeding in pregnancy show no noteworthy genetic correlation. Postpartum hemorrhage due to atony or retained placenta are genetically indistinguishable. (B) Genetic correlations between postpartum bleeding and selected disorders. (C) Genetic correlations between early bleeding and selected traits. Correlations that are significant after accounting for the number of traits tested are highlighted in yellow. Error bars represent the 95% confidence interval. The data sets used for the analysis are described in Supplementary Table 5.