Fig. 1.
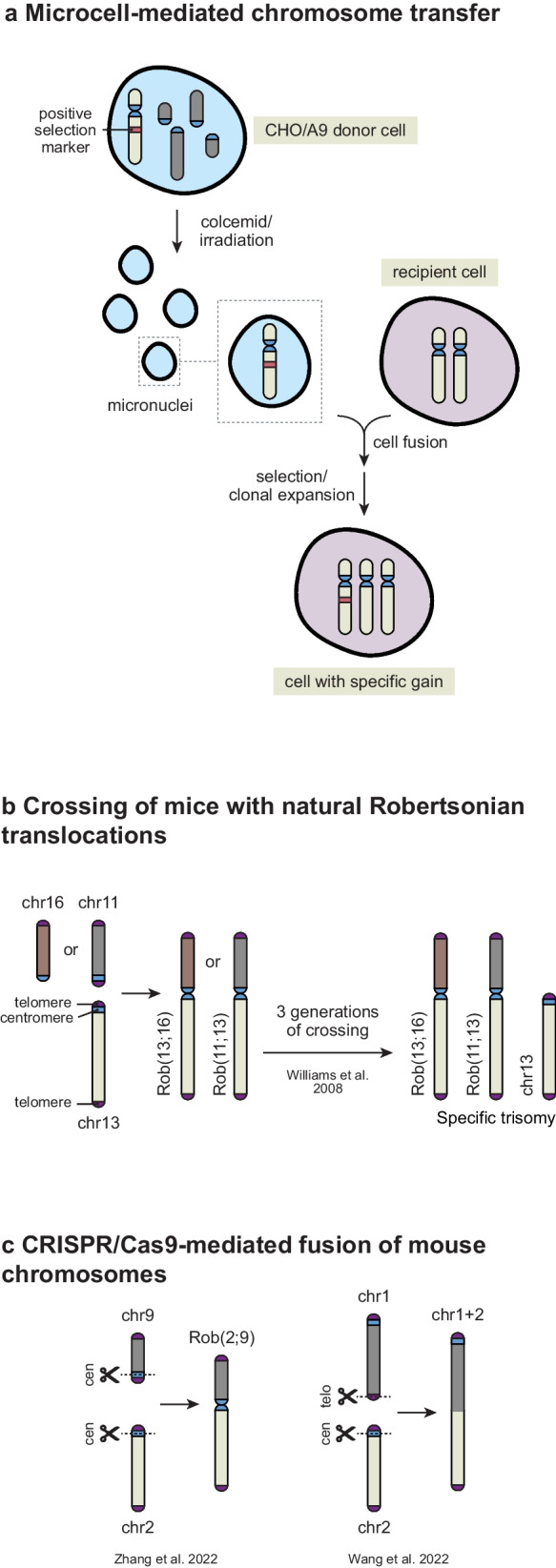
Strategies to introduce an additional chromosome into mammalian cells and mice. a Microcell-mediated chromosome transfer consists of 2 steps: (1) micronuclei formation in donor cells by colcemid treatment or irradiation; and (2) fusion of micronuclei to recipient cells of choice. Hybrid Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) or mouse A9 cells containing a single human chromosome are mostly used as donor cells (Tanabe et al. 2000). A positive selection marker, (often puromycin or neomycin resistance genes), is usually integrated into the chromosome of interest to facilitate the recovery of recipient cells with specific chromosomal gains. b Crossings of mice carrying Robertsonian chromosomes can generate mice and mouse ESCs with specific trisomies (Williams et al. 2008). As starting point, two mouse strains are crossed each carrying a different Robertsonian translocation involving the chromosome of interest (e.g., Rob (13;16) and Rob (11;13)). c CRISPR/Cas9-induced targeted chromosome fusions can generate either Robertsonian-like metacentric chromosomes (Zhang et al. 2022) or a large telocentric fused chromosome (Wang et al. 2022) (Supplemental Table 2). This could be applied to create parental mouse strains carrying specific (viable) chromosome fusions for crossings that eventually generate specific trisomies
