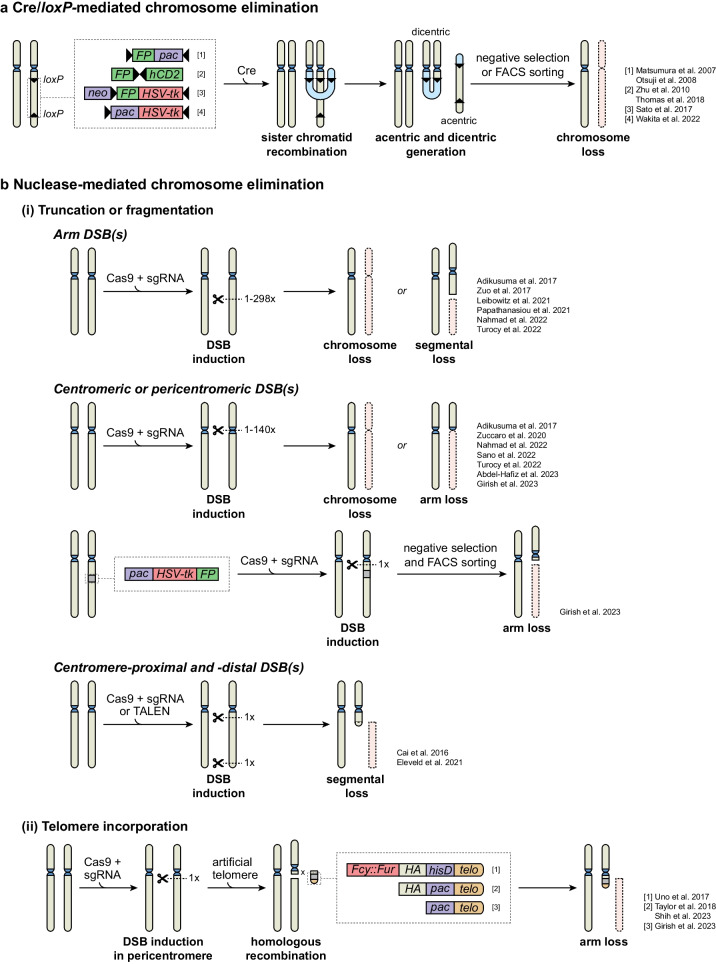
Fig. 2.
Methods to eliminate specific chromosomes. a Two inverted LoxP sites are integrated into a chromosome arm of interest. Upon expression of Cre recombinase after S phase, the two sister chromatids can recombine, generating dicentric and acentric chromosomes that are eventually lost after one or multiple mitoses. An antibiotic resistance gene such as pac (puromycin resistance) or neo (neomycin resistance) is usually inserted between the two loxP sites to facilitate selection of cells harboring loxP integration. To efficiently recover cells with the targeted chromosomal loss, a number of transgenes can be inserted, including ones encoding for fluorescent proteins (FP), cell-surface proteins such as human (h)CD2, or a suicide gene such as herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase (HSV-tk), allowing for FACS sorting or Ganciclovir (GCV)-induced negative selection, respectively. b (i) With one or multiple chromosome-specific sgRNAs, one or multiple DNA double stranded breaks (DSBs) are induced either in the arm or in the (peri-)centromere of the targeted chromosome by CRISPR/Cas9, leading to either whole or partial loss of the targeted chromosome. Integration of a suicide gene (i.e., HSV-tk) in the arm of the targeted chromosome can facilitate selection of cells that have lost the targeted chromosome (arm). Alternatively, CRISPR/Cas9 or TALEN can be used to induce two DSBs flanking the chromosomal region to be deleted. This will lead to ligation of the endogenous telomere to the centromere-proximal break site, leading to specific segmental arm loss. (ii) Telomere-mediated chromosome truncation: CRISPR/Cas9 induces a single DSB near the centromere, and the break is repaired using a repair template containing a positive selection marker (pac or L-histidinol dihydrochloride, hisD), a human telomere sequence (telo), and frequently homology arms (HA) overlapping the break site. The incorporation of a synthetic S. cerevisiae cytosine deaminase-uracil phosphoribosyl transferase fusion gene (Fcy::Fur) outside the HA, can be used to eliminate cells with an off-target integration by 5-fluorocytosine