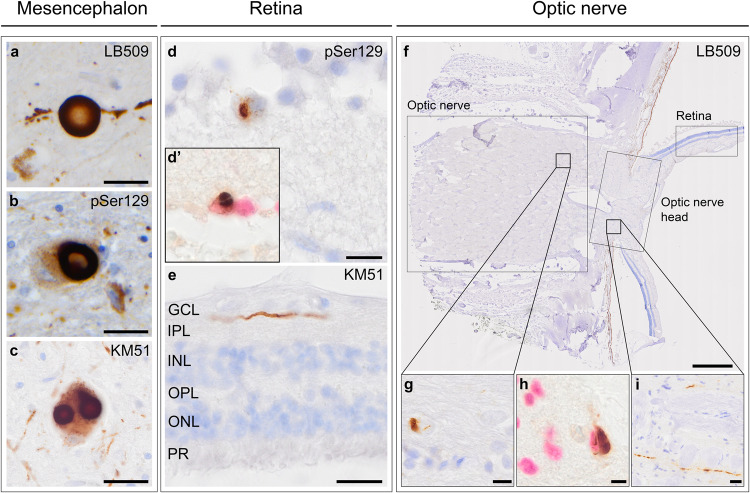
Fig. 1. Localisation and morphology of αSyn pathology in the retina and optic nerve.
Mesencephalon of a Parkinson’s disease case was used as a positive control, here showing immunostaining with a LB509, b pSer129 and c KM51. d pSer129 showed a neuronal staining in a ganglion cell located in the GCL of the retina of a Parkinson’s disease dementia case. d’ αSyn cytoplasmic inclusion (brown) in a ganglion cell was also observed with a nuclear staining for ganglion cells using NeuN (Liquid Permanent Red). e Lewy-like neurites were observed in the IPL of a Parkinson’s disease dementia case. f–h The optic nerve showed αSyn cytoplasmic inclusions in multiple system atrophy (#54). h αSyn cytoplasmic inclusions were observed in oligodendrocytes by co-labelling with anti-SOX-10, which labels nuclei of oligodendrocytes (Liquid Permanent Red). i Multiple system atrophy cases additionally showed Lewy-like neurites in the optic nerve head (#54). Immunostaining is shown with DAB (brown), and nuclei are counterstained with haematoxylin (blue). In (d’) and (h), nuclei are immunolabelled and stained with Liquid Permanent Red. Scale bars: a–c, e, i = 20 µm, d, g = 10 µm, f = 800 µm, h = 5 µm. GCL ganglion cell layer, IPL inner plexiform layer, INL inner nuclear layer, OPL outer plexiform layer, ONL outer nuclear layer, PR photoreceptors.