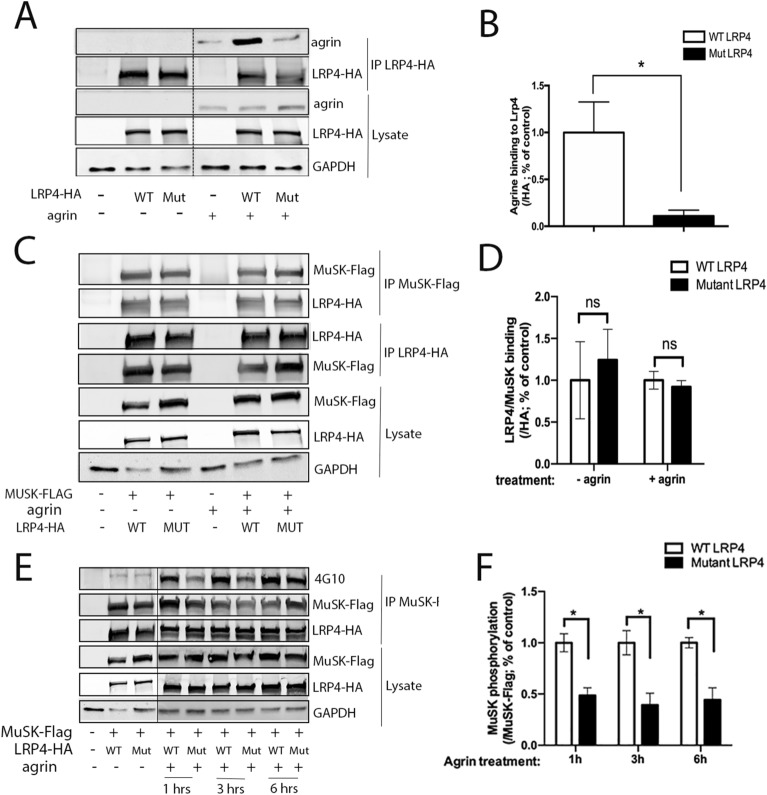
Figure 3.
Alteration of agrin- mediated MuSK signaling induced by mutation in LRP4. (A) The LRP4 mutant inhibits agrin binding in vitro. HEK293T cells were transfected with wild-type (WT) or mutant (Mut) LRP4-HA plasmids. After immunoprecipitation of LRP4-HA and incubation with or without neural agrin (1 μg/ml), the level of agrin binding to LRP4 is followed by immunobloting with anti-agrin antibody. Lines indicate that intervening lanes have been spliced out. (B) Agrin binding to LRP4 shows a significant impairment of agrin binding to LRP4 mutated in vitro. (C) The LRP4 mutant does not affect its binding to its coreceptor MuSK. After co-expression of MuSK-Flag and LRP4-HA in HEK293T cells and immunoprecipitation of MuSK-Flag or LRP4-HA with anti-Flag and anti-HA respectively, the level of MuSK or LRP4 is followed by immunoblotting with anti-Flag or anti-HA antibodies. (D) LRP4 binding to MuSK doesn’t show significant changes of LRP4/MuSK binding when LRP4 is mutated in vitro. (E) The mutation in LRP4 inhibits agrin-mediated regulation of MuSK phosphorylation. HEK293T cells were transfected with MuSK-Flag and WT LRP4-HA or mutant LRP4-HA with or without agrin (0.4 μg/ml) for various times (1, 3 or 6 h). Phosphorylated MuSK was detected by immunoprecipitation of MuSK-Flag and followed by immunoblotting with anti-4G10 (MuSK phosphorylation), anti-Flag and anti-HA antibodies. Lines indicate that intervening lanes have been spliced out. (F) MuSK phosphorylation induced by agrin is significantly impaired when LRP4 is mutated in vitro. p < 0.05, Student’s test. N = 3 blots for each condition. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.