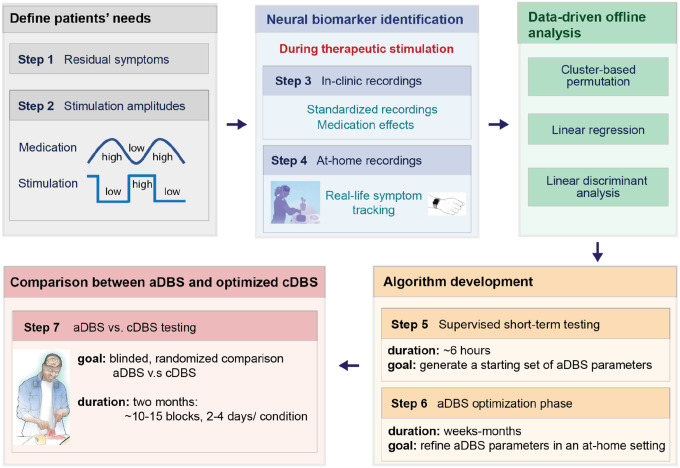
Figure 2. Workflow for data-driven biomarker identification and aDBS implementation.
We employed a workflow consisting of seven steps. These steps involved identifying bothersome symptoms and required stimulation amplitudes for symptom control for each patient (steps 1 and 2), in-clinic and at-home neural recordings with simultaneous symptom monitoring for biomarker identification (steps 3–4) and refining parameters for patient-tailored adaptive algorithms using supervised short-term (step 5) and long-term (step 6) at-home testing. The workflow culminated in blinded, randomized comparisons between cDBS and aDBS in multiple blocks of 2–4 days per condition (total of one month per condition) in patients’ real-life environments (step 7).