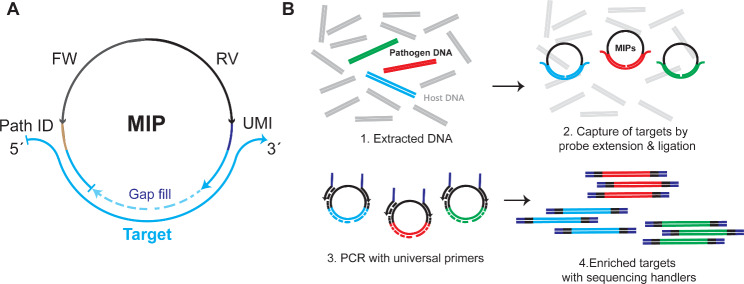
Fig. 1.
General outline of the method. (A) MIP arms (blue) hybridize to the complementary target regions forming an open circle. A polymerase extends the gap in between arms (dotted line) and a DNA ligase is used to close the resulting nick. The MIP backbone contains: FW & RV: Forward & reverse primer binding sites. UMI: Unique molecular identifier. Path ID: Pathogen identifier. (B) (1) Extracted DNA contains few copies of pathogen DNA. (2) Targets are captured by adding MIPs that circularize after extension and ligation templated by the targets. (3) & 4. After exonuclease treatment, reacted probes are amplified with universal primers containing sequencing handlers for downstream library indexing and pooling for short-read single end Illumina sequencing for pathogen identification