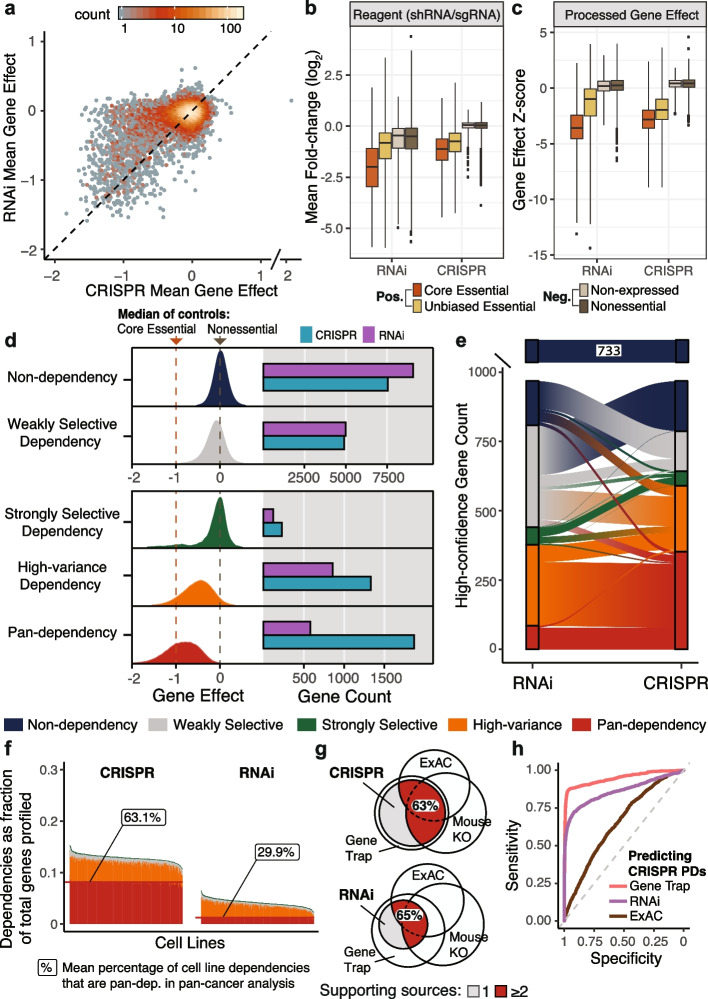
Fig. 1.
CRISPR knockout produces stronger viability effect than RNAi knockdown. a Mean gene effect across 403 cell lines for 15,221 genes overlapping the CRISPR and RNAi datasets. Each axis is divided into 100 bins (2D histogram) and the color of the dots represents the number of data points that fall into each bin. b Log2 fold-change (LFC) values for reagents targeting the same gene are collapsed to gene means per cell line. Boxes represent the distribution of gene mean LFC across all cell lines for genes included in the nonessential control set [24] (738 genes), non-expressed set (10 randomly sampled genes from each cell line with RNAseq log2(TPM + 1) < .2), unbiased essential gene set described in the “Methods” (744 genes), or the core essential control set [24] (208 genes). CRISPR reagents are from the Avana library and RNAi reagents are those used in the DEMETER2-combined [16] RNAi dataset (union of Achilles and DRIVE libraries). Whiskers are extended to 4 times the interquartile range to limit overplotting outliers since over 1.2 million data points are represented. c Unscaled gene effect estimates from CERES (CRISPR) and DEMETER2 (RNAi) were normalized per cell line (Z-score) and grouped into the same control sets and plot parameters from part b. d Each gene (N = 15,221) is included in at least one dependency class. Density plots illustrate the difference in dependency patterns between dependency classes and represent the union of CRISPR gene effects for all genes in each dependency class. The horizontal bars represent the number of genes identified as members of the respective dependency classes. e Mapping between the disjoint CRISPR and RNAi dependency class for each high-confidence gene (N = 1703). f Each cell line (N = 403) is a stacked bar where bar segments represent the proportion of gene dependencies relative to the total number of genes profiled in each cell line (y axis). Labels indicate the mean percent of dependencies per cell line that are classified as pan-dependencies in the overall CRISPR or RNAi dataset. Colors correspond to the gene dependency classifications as indicated in part d. g Intersection of pan-dependencies identified using CRISPR and RNAi datasets with essential genes identified using ExAC, mouse knockout, and gene trap. h Ability to separate genes classified as pan-dependencies in both CRISPR datasets (N = 1339) from genes that were not pan-dependencies in either CRISPR dataset (N = 14,702) using ROC AUC of mean gene trap results for KBM7 and HAP1 (AUC = 0.96), RNAi mean D2-Combined gene effect (AUC = 0.86), and the median of ExAC constrained loss-of-function metrics (AUC = 0.65)