Figure 5.
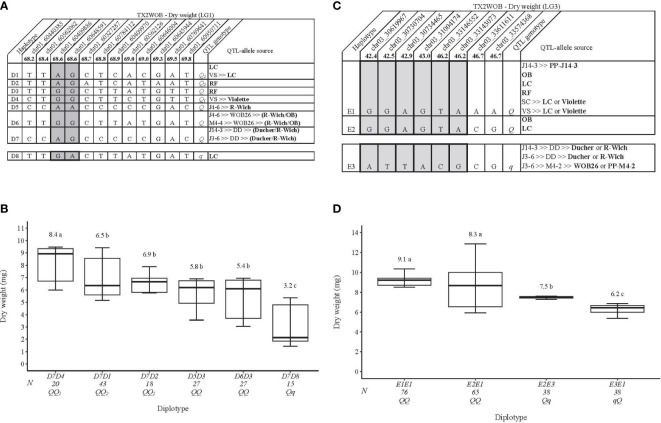
QTL genotypes for dry weight in diploid rose breeding parents with haplotype names, SNP sequences, origin sources, and alleles for predictive SNP markers associated with Q- or q-alleles for increasing or decreasing the dry weight, respectively, are shaded (A, C), and the diplotype effect of the most common haplotypes associated with the dry weight (B, D) at qDWT.TX2WOB-LG1 and qDWT.TX2WOB-LG3, respectively. The Q without a subscript indicates that were not able to categorize this haplotype due to the lack of appropriate diplotype combinations. Means not connected by the same letter are significantly different (p<0.05) within each population using the non-parametric multiple comparison Steel–Dwass test. N = diplotype sample size. LC, ‘Little Chief’; VS, ‘Vineyard Song’; RF, ‘Red Fairy’; OB, ‘Old Blush’; SC, ‘Sweet Chariot’; R-Wich, Rosa wichuraiana.