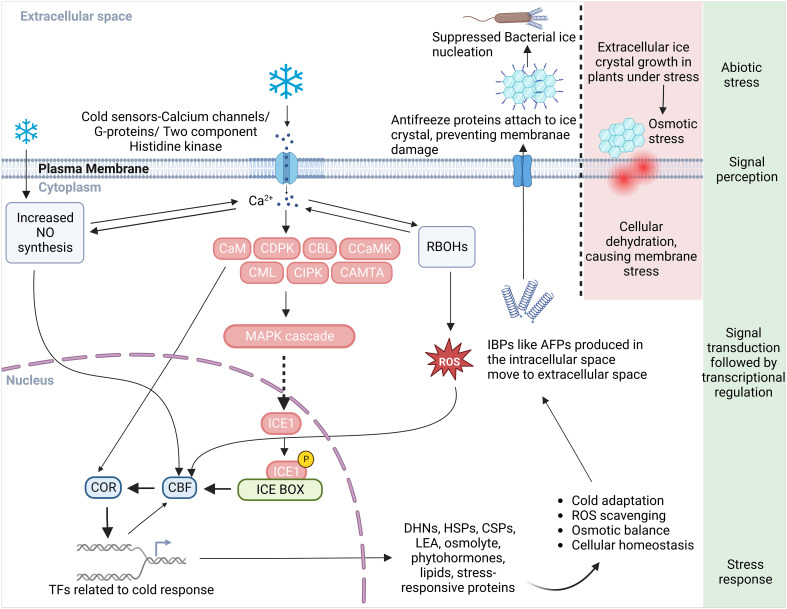
Figure 1.
A schematic diagram illustrating an overview of the cold perception and the Ca2+ mediated cold responsive signal transduction and response pathways in plant. Plasma membrane receptors and membrane rigidification sense the cold stress and initiate a series of downstream reactions. This cascade activates calcium channels/G-proteins, a two-component histidine kinase, and increases Ca2+ influx in the cytoplasm, subsequently stimulating Ca2+-related proteins such as CaM, CDPK, CBL, CCaMK, CML, CIPK, CaMTA, and the MAPK signaling pathway. ICE1 interaction with the signaling cascade instigates the ICE-CBF-COR transcriptome machinery’s response. Proteins responsible for the synthesis of cryoprotectants, PKs, phytohormones, and protective proteins like DHNs, AFPs, HSPs, and CSPs, all crucial in cold adaptation, are encoded by the COR genes. For freeze protection in cold-acclimated plants, the process involves IBP induction, secretion of AFPs into the extracellular space, and attachment to ice crystals to inhibit their growth and to prevent freezing linked with bacterial ice nucleation. In non-acclimated plants lacking IBP, large damaging ice crystals form that can rupture the plasma membrane due to cellular dehydration caused by an osmotic gradient that sequesters intracellular water. An increase in Ca2+ level due to cold stress also activates RBOHs to produce more ROS and prompts NO synthesis necessary for cold adaptation response. The crosstalk between ROS and Ca2+ controls the expression of defense related genes in nucleus. ROS, reactive oxygen species; NO, nitric oxide; RBOH, respiratory burst oxidase homologues; CaM, calmodulin; CDPKs, Ca2+ dependent protein kinases; CBLs, calcineurin B-like proteins; CCaMK, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase; CML, CaM like; CIPK, CBL-interacting protein kinases; CaMTA, CaM-binding transcription activator; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; CBFs, C-repeat binding factors; ICE, inducer of CBF expression; COR, cold-responsive; AFP, anti-freeze proteins; IBP, ice-binding proteins; DHN, dehydrin, HSP, heat shock proteins; CSP, cold shock protein; LEA, late embryogenesis abundant protein; TFs, transcription factors.