Fig. 5.
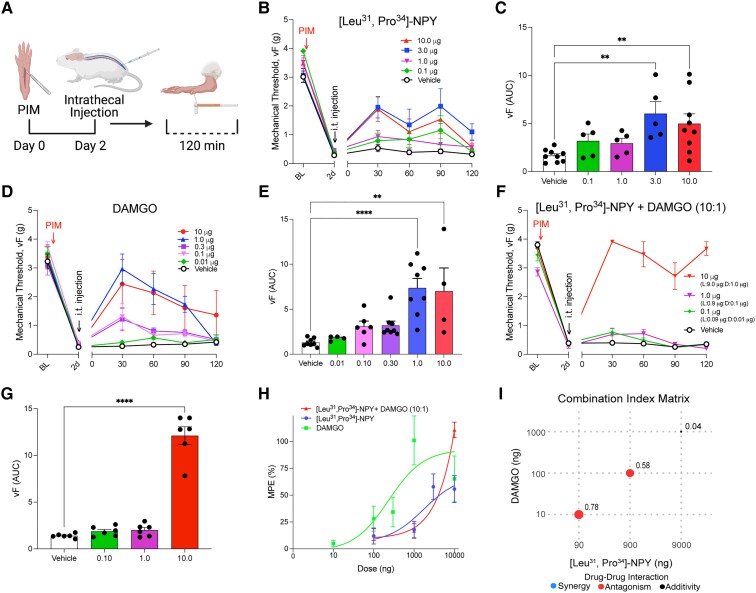
Exogenous Y1R and MOR agonists do not synergistically inhibit acute pain. A) Experimental timeline of PIM, i.t. injections (i.t.) into the mouse to pharmacologically target the spinal cord, and von Frey mechanical threshold behavioral testing. B and C) Intrathecal administration of [Leu31, Pro34]-NPY dose-dependently (0.1, 1.0, 3.0, or 10.0 µg) reduced incision-induced hyperalgesia. n = 5–9 mice/group. One-way ANOVA: F(4, 28) = 4.707, P = 0.0049; Dunnett's multiple comparison tests. D and E) Intrathecal administration of DAMGO dose-dependently (0.01, 0.1, 0.3, 1.0, or 10.0 µg) reduced incision-induced hyperalgesia. n = 4–8 mice/group. One-way ANOVA: F(5, 32) = 8.316, P < 0.0001; Dunnett's multiple comparison tests. F and G) Intrathecal administration of [Leu31, Pro34]-NPY and DAMGO together in a 10:1 combination reduces incision-induced hyperalgesia in an additive manner. n = 6 mice/group. One-way ANOVA: F(3, 20) = 103.6, P < 0.0001; Dunnett's multiple comparison tests. H) Dose–response effects of agonist-induced antihyperalgesia (MPE). I) CI matrix showing Log CI values for MPE from mice treated with the drug combination of [Leu31, Pro34]-NPY and DAMGO. The larger the size of the circle is the higher the CI power. Analyses were performed using SiCoDEA software. Data in B–H are shown as mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01 and ****P < 0.0001.