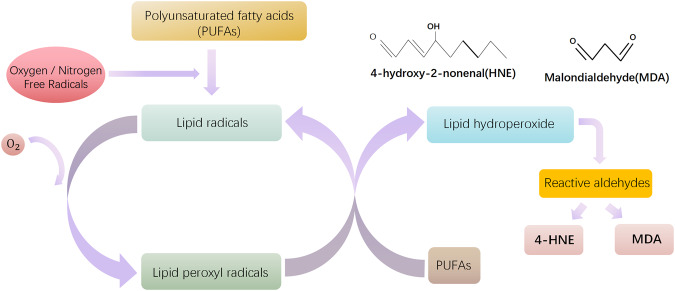
Fig. 1. Simplified schematic illustrating the peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs).
Free radical-mediated oxidation lipid peroxidation includes three steps: initiation, propagation, and termination. In the initiation phase, ROS/ RNS free radicals react with PUFAs and abstract an allylic hydrogen thus forming lipid radicals. In the propagation phase, the lipid radicals react with oxygen and form lipid peroxyl radicals, and then lipid peroxyl radicals react with PUFAs to form new radicals and lipid hydroperoxides. In the termination phase, the propagation can be blocked by antioxidants or lipid radicals by donating a hydrogen atom to lipid peroxyl radicals resulting in the formation of nonradical products. Due to the instability of lipid hydroperoxides, they may degrade into secondary products. 4-HNE and MDA are the main products among the many reactive aldehydes.