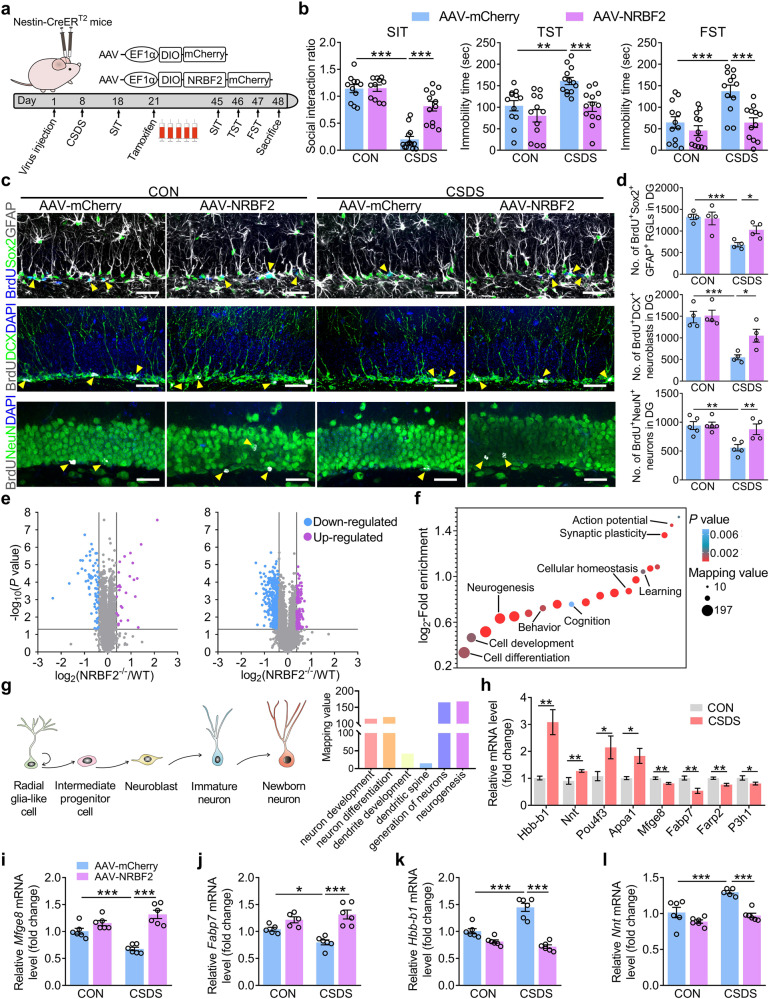
Fig. 8. Overexpression of NRBF2 in aNSCs rescues disrupted neurogenesis-related protein network of DG induced by chronic stress.
a Timeline of experiments. b Behavioral tests of SIT, TST, and FST on control and CSDS-exposed mice treated with AAV-mCherry or AAV-NRBF2 in DG aNSCs (n = 11–13 mice per group). c, d Representative images (c) and quantification (d) of BrdU+Sox2+GFAP+ RGLs, BrdU+DCX+ neuroblasts, and BrdU+NeuN+ neurons in the DG (n = 4–5 mice per group). Yellow arrows indicate BrdU+ and marker+ cells. Scale bars, 30 μm. e A total of 98/6791 proteins and 563/3374 phosphopeptides were statistically up- or downregulated in NRBF2−/− mice (n = 3 mice per group). f The significant changes in expression or phosphorylation of proteins induced by NRBF2 deletion were most dominantly enriched in biological processes that involved neurogenesis, action potential, and synaptic plasticity. g A schematic diagram of each phase during adult hippocampal neurogenesis (left). Numbers in histograms are mapping values, i.e., the sum of phosphopeptides involved in neurogenesis (right). h CSDS upregulated the level of Hbb-b1, Nnt, Pou4f3, and Apoa1 mRNA, but downregulated the level of Mfge8, Fabp7, Farp2, and P3h1 mRNA in the DG (n = 5–8 mice per group). i–l The level of Mfge8 (i), Fabp7 (j), Hbb-b1 (k), and Nnt (l) mRNA in the DG of control and CSDS-exposed mice treated with AAV-mCherry or AAV-NRBF2 (n = 5–6 mice per group). Data are presented as means ± SEM and analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test (b, d, i–l) or two-sided unpaired t-test (h), or Fisher’s exact test (e–g). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.