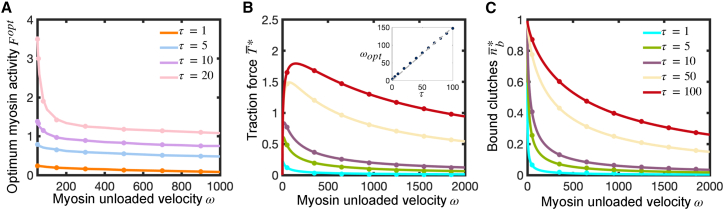
Figure 5.
Traction force produced by a strong-motor protrusion on rigid substrates reaches a maximum at an intermediate value of the myosin load-free velocity parameter . (A) Optimum myosin activity parameter for maximum traction force on rigid substrates as a function of for four different values of the clutch kinetic parameter . The optimum activity monotonically decreases with and . (B and C) Dimensionless time-averaged traction force (B) and average fraction of bound clutches (C) for a strong-motor protrusion () on rigid substrates (), as a function of for five different values of . Force transmission shows a biphasic dependence on the parameter , with an optimum that increases linearly with (see inset in (B)). Number of bound clutches increases monotonically with and . Solid lines correspond to the analytical solutions of the mean-field model (Eqs. S55 and S57), and symbols are the solutions of the stochastic model. Near-perfect agreement is found between analytical and stochastic solutions. To see this figure in color, go online.