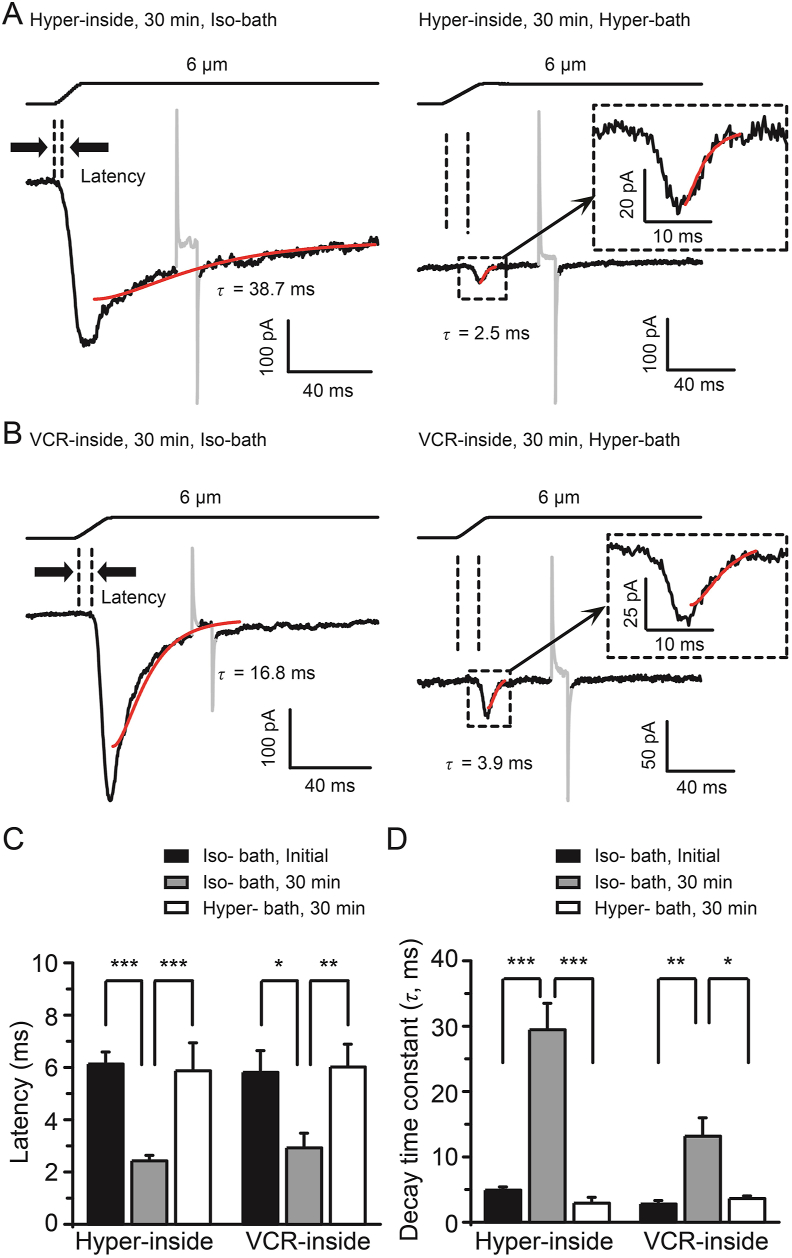
Figure 7.
The VCR-induced changes in the properties of PIEZO2 MA currents were reversed by hypertonic bath solution. (A) Representative traces of PIEZO2 MA currents elicited by a 6-μm membrane displacement at 30 min (bottom) after establishing whole-cell mode patch recording with hypertonic internal solution (420 mOsm) (Hyper-inside) and isotonic bath solution (left, Iso-bath) or hypertonic bath solution (right, 420 mOsm) (Hyper-bath). (B) Representative traces of PIEZO2 MA currents elicited under the same conditions as in (A) but recorded with isotonic internal solution containing 5 μmol/L VCR (VCR-inside). In (A) and (B), the onset latency for evoking PIEZO2 MA currents is indicated by dish lines, the inactivation kinetics are fitted with a single exponential function (red line) and the decay time constants (τ values) are shown. Insets in the right panels in (A) and (B), extended scale for the boxed region is shown. Summary data of the latency (C) and decay time constants (τ) (D) of PIEZO2 MA currents under the above conditions are shown. Hypertonic bath solution (Hyper-bath) reversed the changes in the properties of PIEZO2 MA currents induced by osmotic swelling (Hyper-inside) and VCR (VCR-inside). Data are shown in mean ± SEM, n = 21 and 15 (Hyper-inside, Iso-bath, initial), 21 and 20 (Hyper-inside, Iso-bath, 30 min), 7 and 7 (Hyper-inside, Hyper-bath, 30 min), 10 and 11 (VCR-inside, Iso-bath, initial), 8 and 11 (VCR-inside, Iso-bath, 30 min) and 5 and 5 (VCR-inside, Hyper-bath, 30 min) in (C) and (D), respectively; ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001.