Figure 4.
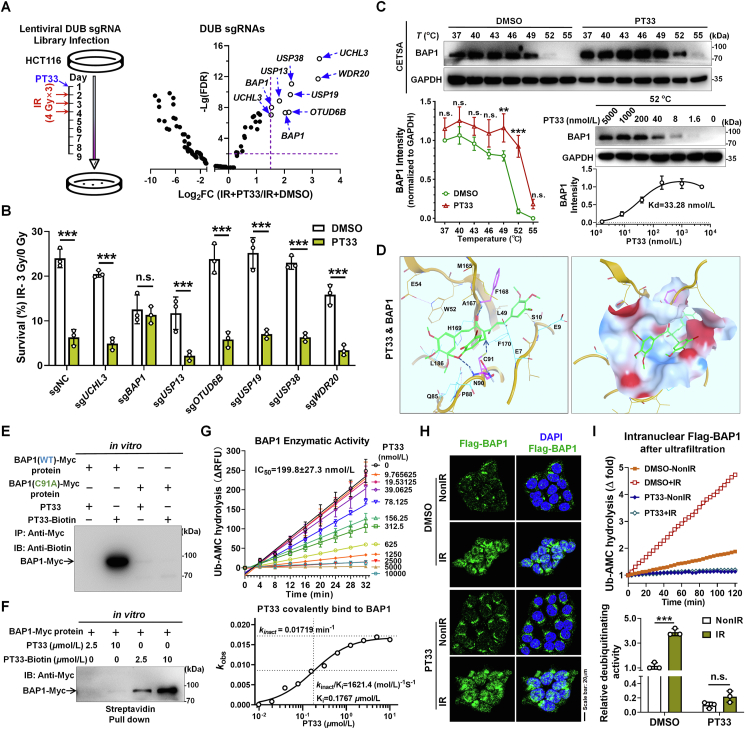
CRISPR-Cas9 screening identified BAP1 as a potential target of PT33. (A) Left: treatment scheme of DUBs sgRNA library screening experiment; right: relative abundance of individual genes from CRISPR-Cas9 screen. Genes with Log2FC > 1.5 and –Lg(FDR) > 2 were considered as potential target of PT33 to sensitize CRC cells to IR. (B) Colony formation assay detecting survival ratio of HCT116 cells knocking out corresponding genes treated with PT33 and IR. (C) PT33 binding to BAP1 was evaluated by cellular thermal shift assay. Upper and left below: HCT116 cells were treated with PT33 (5 μmol/L) for 1 h incubated in indicated temperature for 3 min; right below, HCT116 cells were treated with indicating concentrations of PT33 for 1 h and incubated in 52 centigrade for 3 min. Immunoblot detecting BAP1 intensity, GAPDH as loading control. (D) 3D presentation of the predicted binding mode of PT33 with BAP1 by molecular docking. Hydrophobic and hydrophilic residues of BAP1 were labeled by dashed lines (upper); and the surface is shown in below. PT33 is shown in green stick. (E, F) In vitro pull-down assays detecting PT33 and BAP1 covalent interaction. Purified myc-BAP1 was incubated with PT33 or PT33–Biotin. (E) BAP1 was immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted by biotin antibody. (F) Streptavidin pull down of biotin and immunoblotted by Myc antibody. (G) In vitro BAP1 deubiquitinating activity of BAP1 measured by UB-AMC hydrolysis assay. Upper: fluorescence-time curve; Below: the curve of covalent binding Kobs to determinate the covalent inactivation rate (kinact) and reversible binding affinity Ki for PT33 against BAP1. (H) HCT116 cells were treated with PT33 (125 nmol/L) for 12 h followed by 6 Gy IR, 6 h later, Flag-BAP1 was detected by IF assay. (H) HCT116 cells were treated as indicated and nuclear Flag-BAP1 was enriched and ultrafiltration, followed by Ub-AMC hydrolysis assay. Upper: representative fluorescence-time curve; below: statistical analysis of relative DUB activity. (B, C, G and I) Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 3). Statistical significance was determined by (B, I) Student's t test, (C) two-way ANOVA (n.s., not significant; ∗∗∗P < 0.001).