Fig. 2.
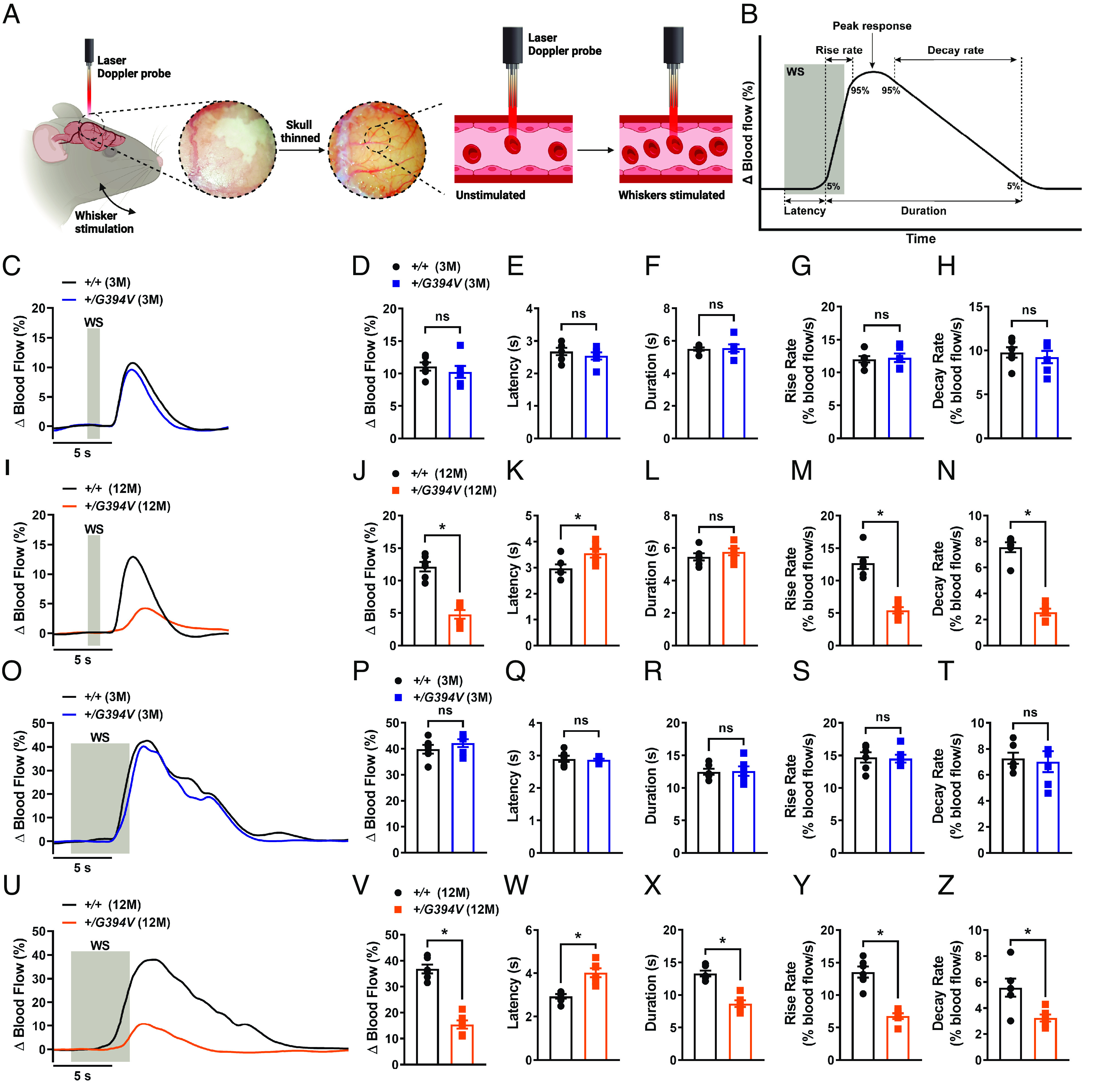
Age-dependent impairment of functional hyperemia in Col4a1+/G394V mice. (A) Illustration demonstrating the functional hyperemia assessment procedure in the mouse somatosensory cortex. (B) Illustration demonstrating the parameters that were analyzed. (C and D) Representative traces (C) and summary data (D) showing the increase in blood flow following 1-s contralateral whisker stimulation (WS) in 3-M-old Col4a1+/+ and Col4a1+/G394V mice (n = 6 animals per group, ns = not significant, unpaired t test). (E–H) Latency (E), duration (F), rise rate (G), and decay rate (H) were also analyzed (n= 6 animals per group, ns = not significant, unpaired t test). (I and J) Representative traces (I) and summary data (J) showing the increase in blood flow following 1-s contralateral WS in 12-M-old Col4a1+/+ and Col4a1+/G394V mice (n = 6 animals per group, *P < 0.05, unpaired t test). (K–N) Latency (K), duration (L), rise rate (M), and decay rate (N) were also analyzed (n = 6 animals per group, *P < 0.05, ns = not significant, unpaired t-test). (O and P) Representative traces (O) and summary data (P) showing the increase in blood flow following 5-s contralateral WS in 3-M-old Col4a1+/+ and Col4a1+/G394V mice (n = 6 animals per group, ns = not significant, unpaired t-test). (Q–T) Latency (Q), duration (R), rise rate (S), and decay rate (T) were also analyzed (n= 6 animals per group, ns = not significant, unpaired t-test). (U and V) Representative traces (U) and summary data (V) showing the increase in blood flow following 5-s contralateral WS in 12-M-old Col4a1+/+ and Col4a1+/G394V mice (n = 6 animals per group, *P < 0.05, unpaired t test). (W–Z) Latency (W), duration (X), rise rate (Y), and decay rate (Z) were also analyzed (n = 6 animals per group, *P < 0.05, unpaired t test).
