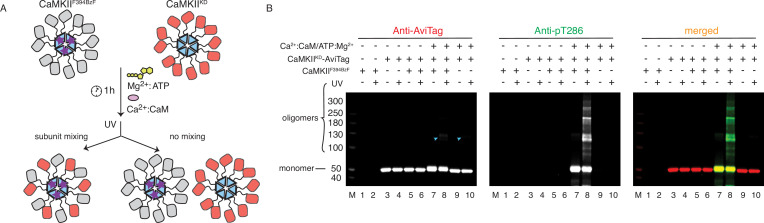
Figure 3. CaMKII holoenzymes do not mix during activation.
(A) Schematic representation of the experiment performed in panel (B) and possible outcomes. (B) Western blot detection of potential CaMKIIKD-AviTag incorporation in CaMKIIF394BzF holoenzymes. Lane 1 – CaMKIIF394BzF, lane 2 - CaMKIIF394BzF treated with UV, lane 3 - CaMKIIKD-AviTag, lane 4 - CaMKIIKD-AviTag treated with UV, lane 5 - CaMKIIF394BzF incubated with CaMKIIKD-AviTag, lane 6 - CaMKIIF394BzF incubated with CaMKIIKD-AviTag, then UV treated, lane 7 - CaMKIIF394BzF incubated with CaMKIIKD-AviTag and activation stimuli (Ca2+:CaM and Mg2+:ATP), lane 8 - CaMKIIF394BzF incubated with CaMKIIKD-AviTag and activation stimuli (Ca2+:CaM and Mg2+:ATP), then UV treated, lane 9 - CaMKIIKD-AviTag incubated with activation stimuli (Ca2+:CaM and Mg2+:ATP), lane 10 - CaMKIIKD-AviTag incubated with activation stimuli (Ca2+:CaM and Mg2+:ATP), then UV treated. Blue arrowheads indicate nonspecific, UV-induced, dimerization of CaMKIIKD-AviTag, independent of BzF.