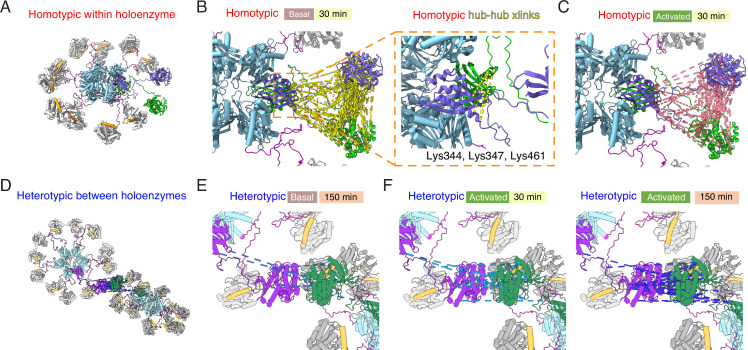
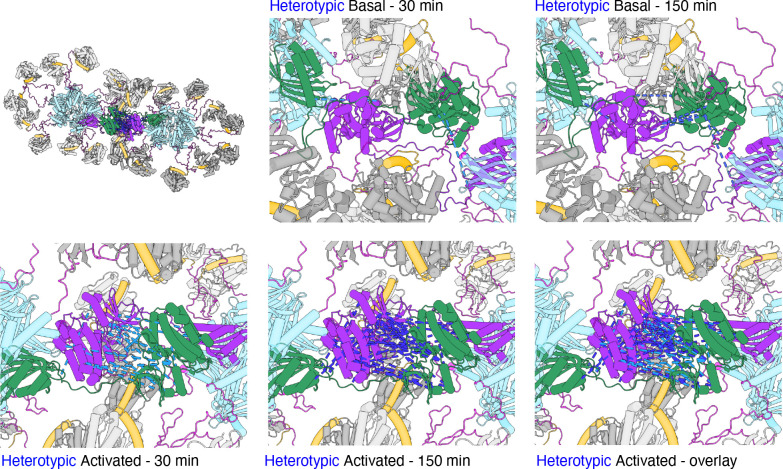
Figure 5. Mapping crosslinks onto holoenzyme structure.
(A) Holoenzyme structure with two neighboring subunits (green and purple) indicated (PDB: 5u6y). Hub domain is in light blue, regulatory segment (docked) in orange. (B) Basal crosslinks between homo-isotypes (30 min incubation, 136 crosslinks as dashed yellow lines) plotted onto the holoenzyme as intersubunit interactions. Inset shows the 5 homo-isotopic crosslinks found for interactions between neighboring hub domains. (C) Crosslinks between homo-isotypes in activated conditions (30 min, 85 crosslinks as pink dashed lines) showed a similar pattern to the basal condition. (D) Two holoenzymes arranged to allow kinase-kinase contacts to form (between green and purple subunits). (E) Sparse heterotypic crosslinks (8 in total, blue dashed lines) in the basal condition after 150 min. All heterotypic crosslinks involve the kinase domain. (F) In activating conditions, 15 heterotypic kinase-kinase interactions were detected after 30 min (out of 20 total). Over 150 min activation, 32 heterotypic kinase-kinase interactions were found (out of 43 total).