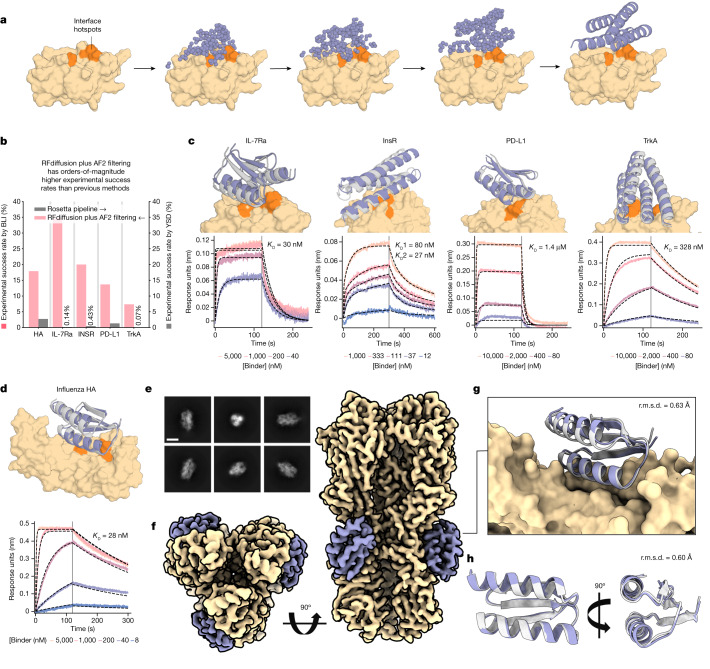
Fig. 6. De novo design of protein-binding proteins.
a, RFdiffusion generates protein binders given a target and specification of interface hotspot residues. b, De novo binders were designed to five protein targets; Influenza A H1 HA, IL-7Rα, InsR, PD-L1 and TrkA and hits with BLI response greater than or equal to 50% of the positive control were identified for all targets. For IL-7Rα, InsR, PD-L1 and TrkA, RFdiffusion has success rates roughly two orders of magnitude higher than the original design campaigns. We attribute one order of magnitude to RFdiffusion, and the second to filtering with AF2 (estimated success rates for previous campaigns if AF2 filtering had been used: HA, 0%; IL-7Rα, 2.2%; InsR, 5.5%; PD-L1, 3.7%; TrkA, 1.5%). c, For IL-7Rα, InsR, PD-L1 and TrkA, the highest affinity binder is shown above a BLI titration series. Reported KD values are based on global kinetic fitting with fixed global Rmax. d, The highest affinity HA binder, HA_20, binds with a KD of 28 nM. c,d, Yellow or orange, target or hotspot residues; grey, design model; purple, AF2 prediction (r.m.s.d. AF2 versus design). Binders: IL7Ra_55 (2.1 Å), InsulinR_30 (2.6 Å), PDL1_77 (1.5 Å), TrkA_88 (1.4 Å) (left to right in c) and HA_20 (1.7 Å) (d). e, Cryo-EM 2D class averages of HA_20 bound to influenza HA, strain A/USA:Iowa/1943 H1N1 (scale bar, 10 nm). f, 2.9 Å cryo-EM 3D reconstruction of the complex viewed along two orthogonal axes. HA_20 (purple) is bound to H1 along the stem of all three subunits. g, The cryo-EM structure of the HA_20 binder in complex closely matches the design model (r.m.s.d. to RFdiffusion design, 0.63 Å; yellow, influenza HA). h, Structure of the HA_20 binder alone superimposed on the design model viewed along two orthogonal axes. For cryo-EM panels, yellow, Influenza H1 map and/or structure; grey, HA_20 binder design model; purple, HA_20 binder map or structure.