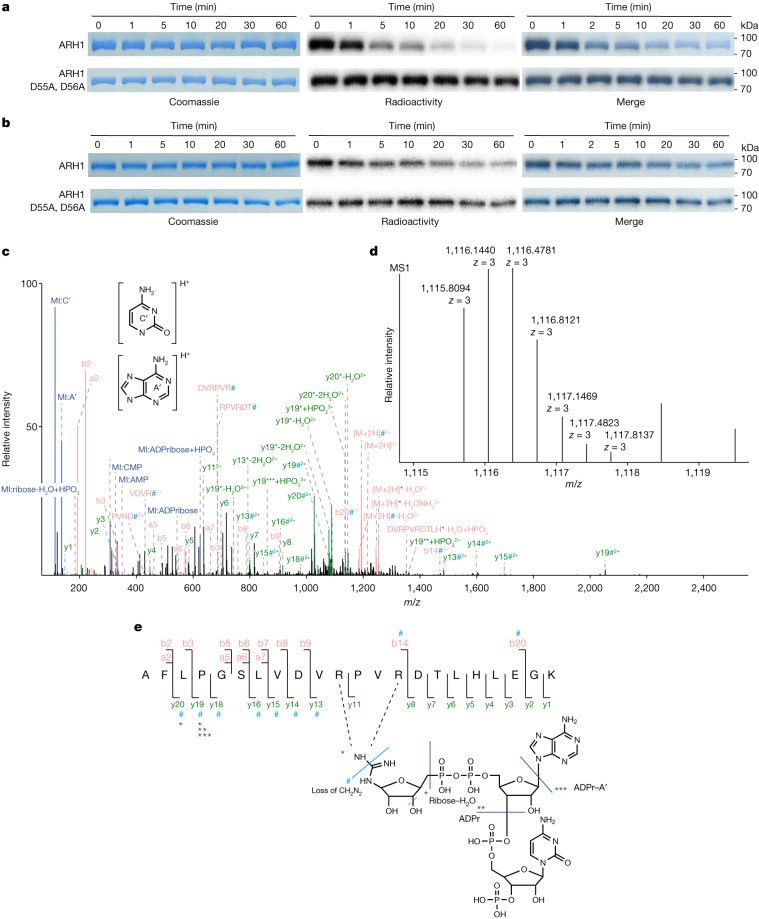
Fig. 3. Identification of RNAylation sites of rS1.
a,b, Specific removal of ADP-ribosylation and RNAylation by ARH1 (n = 3). Schematics of the reaction are shown in Extended Data Fig. 4c,d. Enzyme kinetics of ARH1 in the presence of ADP-ribosylated (a) or RNAylated (b) protein rS1 were analysed by SDS–PAGE. Mutation of the catalytically important residues D55 and D56 abolished the removal of ADP-ribosylation and RNAylation. c-e, Tandem MS-based identification of RNAylated rS1 peptide. c, The MS/MS fragment ion spectrum (spectrum ID: 23723) of RNAylated rS1 peptide AFLPGSLVDVRPVRDTLHLEGK carrying ADPr plus cytidine monophosphate and a 3′ phosphate group. The spectrum shows marker ions (MI) of adenine (A′) and cytosine (C′), adenosine monophosphate (AMP), cytidine monophosphate (CMP), ribose–H2O and ADPr. The precursor ion ([M + 2H]2+) and fragment ions y13–y16, y18–y20, b14 and b20 show a specific loss of mass of 42.021798 Da (#), which can be explained by the loss of CH2N2 at the modified Arg31. Precursor ions, y13, y19 and y20 are shifted by the mass of ribose–H2O (*). The spectrum also shows precursor ions and y19 being shifted by ADPr with (**) and without (***) the loss of adenine. Blue, MI; red, precursor ions, internal fragment ions, b-type fragment; green, y-type fragment ions. d, Isotopic peak pattern of the precursor ion as detected in the MS precursor ion scan for the MS/MS spectrum shown in c. e, Sequence and RNA adduct representation of the RNAylated peptide shown in c and d, including annotations of unshifted fragment ions and fragment ions showing arginine loss (#), as well as ribose–H2O (*), ADPr (**) and ADPr–adenine (***). The fragmentation products of the ADPr + CMP + 3′-phosphate adduct observed in the MS/MS spectrum shown in c are indicated in the structure by light blue (mass loss) and dark blue (mass adducts) lines.