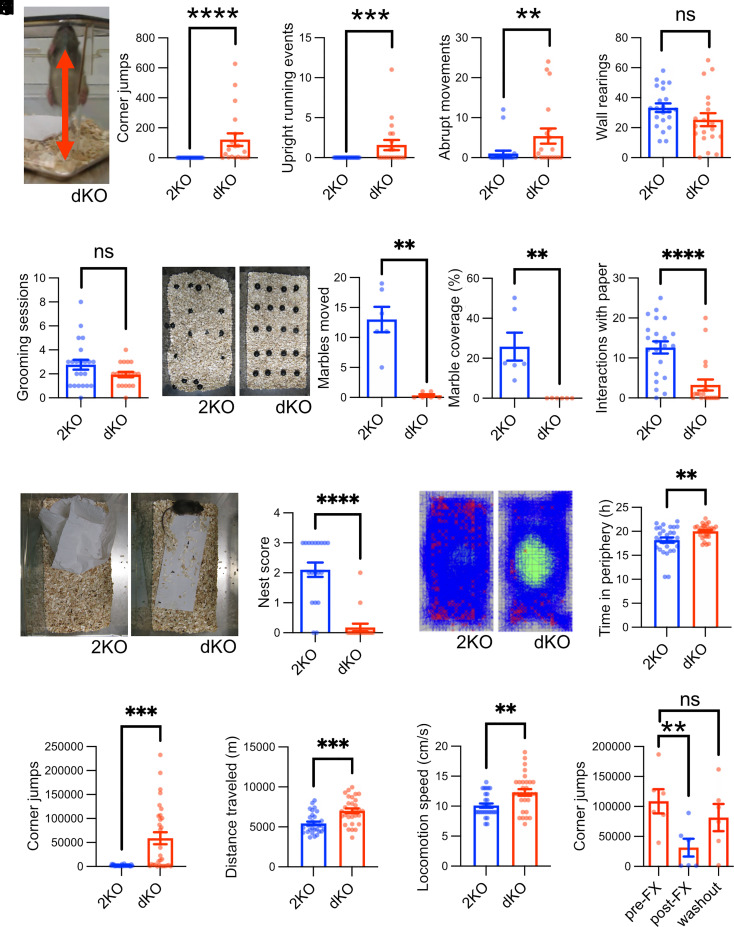
Fig. 1.
Loss of intersectins leads to hyperactivity and obsessive stereotypic behavior. (A–E) Intersectin dKO mice display behavioral abnormalities including repetitive jumping behavior. Mice were observed in their home cage environment for 10 min, and the number of corner jumps (A), episodes of upright running (B), abrupt movements (C), rearings at the wall (D), and grooming episodes (E) were scored [N(2KO) = 22 mice, N(dKO) = 19 mice; Mann–Whitney test or unpaired two-tailed t test; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, ns: not significant]. (F) Intersectin dKO mice fail to bury marbles. Mice were placed in a cage with marbles for 30 min. Afterward, the percentage of marble area covered with bedding material and the number of marbles moved were quantified (N = 6 mice per genotype; Mann–Whitney test; **P < 0.01). (G and H) Intersectin dKO mice fail to build nests. Mice were either supplied with a fresh paper towel and observed for 10 min (G) or left in the cage for 24 h (H). For (G) episodes of occupation with paper were scored and for (H) the quality of nest building was graded with 4 being the top score [G: N(2KO) = 22 mice, N(dKO) = 19 mice; unpaired two-tailed t test; ****P < 0.0001; H: N(2KO) = 19 mice, N(dKO) = 17 mice; Mann–Whitney test; ****P < 0.0001]. (I–L) Infrared-beam-based tracking confirms obsessive behavior of dKO mice and reveals hyperactivity. Mice were tracked in xyz for 24 h via infrared beams (see representative images with tracks in blue and positions of rearing/jumping in red). The time spent in the periphery of the cage (I), the number of z beam breaks in cage corners indicative of high rearing or jumping (J), the distance traveled (K), and the locomotion speed (L) were quantified (N = 30 mice per genotype; Mann–Whitney test or unpaired two-tailed t test; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). (M) The OCD medication fluoxetine rescues obsessive behavior of dKO mice. dKO mice with obsessive jumping behavior were treated with fluoxetine for 3 wk, and the number of corner jumps was recorded for 24 h via infrared beams prior to the treatment, immediately after the treatment, and 5 to 6 wk after the treatment (washout). (N = 6 mice; Friedman test with Dunn's multiple comparison test; **P < 0.01, ns: not significant).