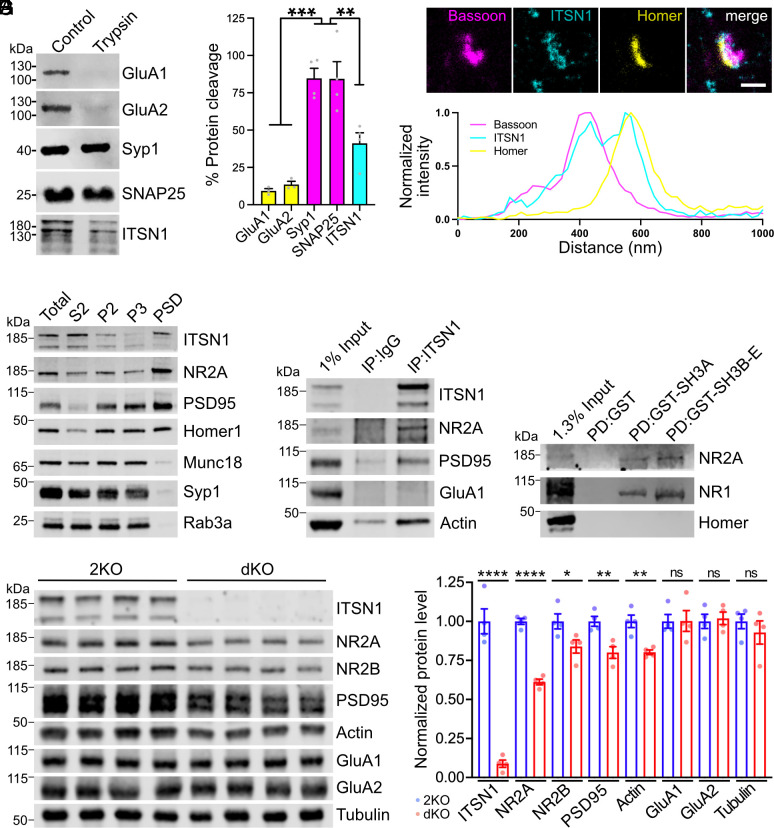
Fig. 4.
Intersectin localizes to the postsynapse and stabilizes NMDA receptors. (A) Tryptic digest of synaptosomes reveals postsynaptic localization of ITSN1. Synaptosomes were left untreated or incubated with trypsin and analyzed by immunoblotting. For quantification, trypsin-treated samples were normalized to untreated controls (N = 3 to 4 independent experiments; one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test; ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01). (B) Three-channel time-gated STED confirms postsynaptic localization of ITSN1. (Top) Representative image of wild-type neurons immunolabeled with antibodies against the presynaptic marker bassoon, the postsynaptic marker homer, and ITSN1 (scale bar: 500 nm.) The white line indicates the position of the normalized fluorescent intensity depicted below. (C) ITSN1 is part of the PSD. Wild-type mouse brain homogenates were subjected to subcellular fractionation, and equal protein amounts of total homogenate (T), cytosolic fraction (S2), synaptosomes (P2), synaptosomal membranes (P3), and PSD were compared by immunoblotting with the indicated markers. (D) ITSN1 forms complexes with NMDA receptors, PSD95 and actin. Coimmunoprecipitation of ITSN1/NMDAR/PSD95/actin complexes from synaptosomal membranes using ITSN1-specific antibodies. Analysis by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (E) Intersectin SH3 domains bind NMDA receptors. GST-intersectin-SH3 domains or GST were incubated with synaptosomal lysate. Analysis by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (F and G) Reduced levels of NMDA receptor subunits in dKO synapses. (F) Immunoblotting for postsynaptic proteins using synaptosomal membrane fractions. Tubulin was used as loading control. (G) Quantification of protein levels normalized to tubulin. For each protein, expression levels from dKO lysates are normalized to 2KO control (N = 4 mice per genotype; unpaired two-tailed t test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001, ns: not significant).