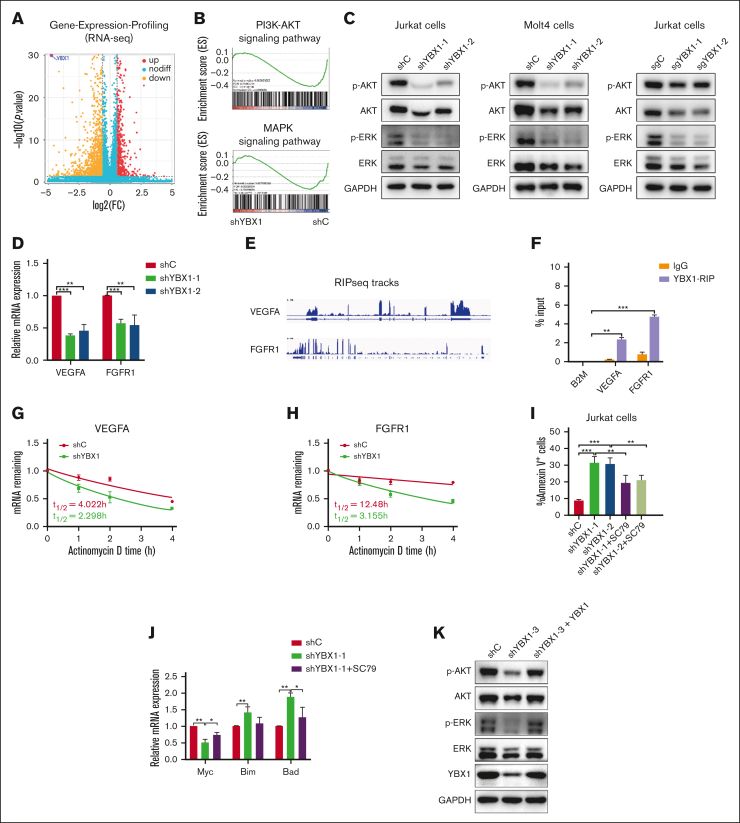
Figure 6.
YBX1 regulates the AKT and ERK signaling pathways in T-ALL cells. (A) Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes in RNA-seq at day 3 after knockdown of YBX1 in Jurkat cells. (B) Enrichment of genes in the PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways using gene set enrichment analysis. (C) Whole cell lysates collected from shC and shYBX1 groups 3 days after infection were analyzed. Western blot was performed to detect the protein expression of p-AKT, total AKT, p-ERK, and total ERK in Jurkat and Molt4 cells. (D) qRT-PCR analysis of mRNA expression of VEGFA and FGFR1. (E) RIP sequencing integrative genomics viewer (IGV) tracks of selected differential gene expression (DEGs) in GSE159153. (F) YBX1 RIP-qPCR analysis showing YBX1 binding to VEGFA and FGFR1 mRNA in HEK293T cells. (G-H) The mRNA half-life of VEGFA (G) and FGFR1 (H) in HEK293T cells. (I-J) Jurkat cells were pretreated with SC79 (1 μg/mL) for 24 hours 2 days after transduction with lentiviruses expressing shRNAs. The percentage of apoptosis was detected via flow cytometry (I), and the mRNA expression of apoptosis-related genes was detected via qRT-PCR (J). (K) Protein expression of p-AKT, total AKT, p-ERK, and total ERK in Jurkat cells was detected via western blot. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.