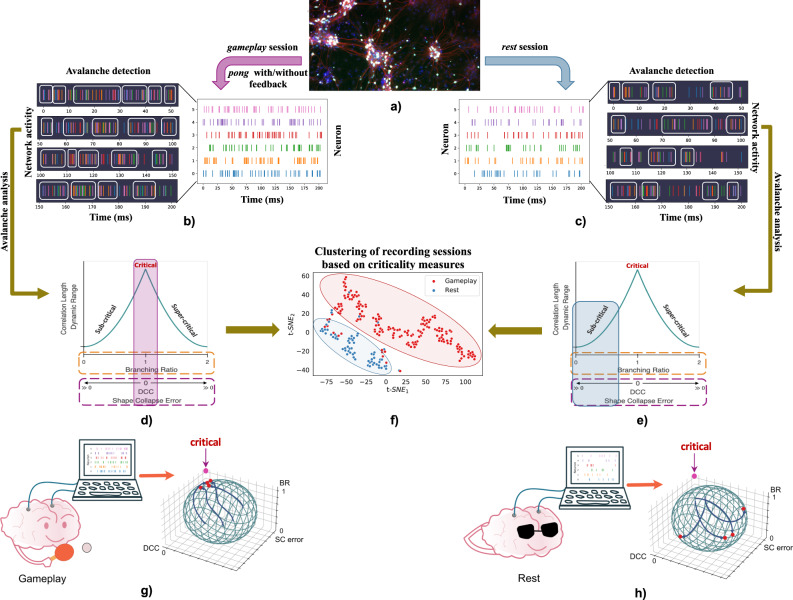
Fig. 1. Schematic overview of study.
a) Showing cortical cells harvested from embryonic rodents. b) & c) The recorded population activity from these cortical cells is then binned to 50 ms bins during both Gameplay and Rest sessions. The neuronal avalanches are cascades of network activity that surpass a certain activity threshold for a certain duration of time, which are then extracted by bin. d) & e) Avalanches are utilized to examine the criticality metrics in the neuronal network’s activity patterns to identify the working regime of each recording in terms of being sub-, super-, or near-critical. f) The same measures of criticality are used to cluster the recordings between two groups of Gameplay and Rest. g) & h) Illustration of the experimental pipeline in which cultured cortical networks are recorded during Gameplay and Rest states. The recorded neuronal activities are then employed to extract the 3 metrics of criticality (namely Branching Ratio (BR), Deviation from Criticality Coefficient (DCC), and Shape Collapse error (SC error)) which are found to move towards the critical point during Gameplay g) and move further from that point during Rest h).