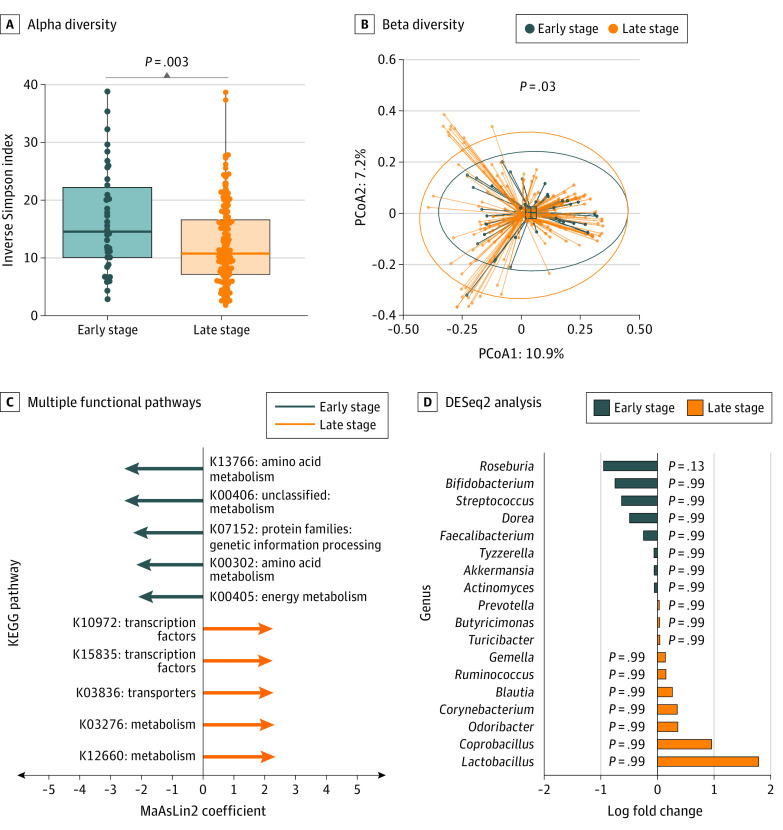
Figure 3. Gut Microbial Diversity Among Patients With Early-Stage vs Late-Stage Melanoma .
A, Gut microbiome profiling showed significantly greater alpha diversity (P = .003, analysis of variance [ANOVA] with covariates) in patients with early-stage melanoma. Boxes represent the median Inverse Simpson Index and IQR; whiskers extend from minimum to maximum values up to 1.5 times above or below the IQR. B, Beta diversity analysis showed a significant difference (P = .03, permutational multivariate ANOVA controlled for covariates). Dots indicate individual samples within a 95% CI circle based on the t-distribution to represent the Euclidean distance from the centroid. PCoA1 indicates principal component analysis axis 1; PCoA2, principal component analysis axis 2. C, Multiple functional pathways were found to be differentially enriched between early-stage and late-stage melanoma samples. MaAsLin2 indicates microbiome multivariable associations with linear models. D, DESeq2 analysis of known bacterial genera that affect response to immunotherapy was performed, with Roseburia demonstrating a nonsignificant higher proportion in patients with early-stage melanoma (P = .13, false discovery rate applied after filtering for selected genera). KEGG indicates Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.