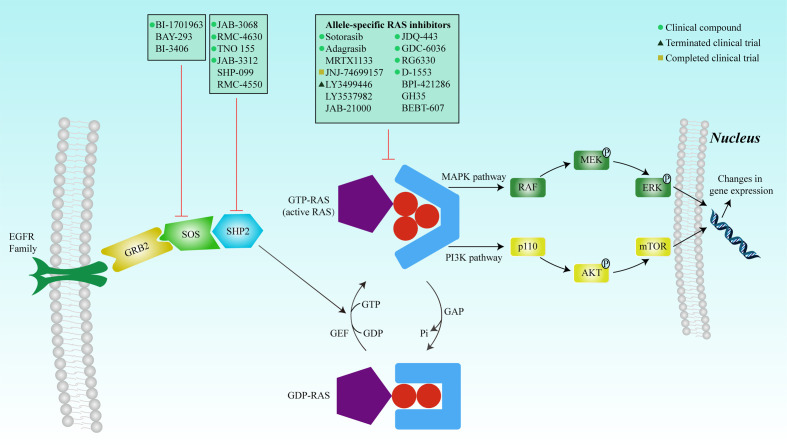
Figure 2.
RAS mutation activates the protein, and the complex formed with GTP binds to the Ras-binding domain of the effector protein (RAF, PI3K, and RALGDS) to activate the MAPK and PI3K signaling pathways, respectively. The signals are transduced into the nucleus to regulate gene expression, thereby affecting cell proliferation and survival. Inhibition of SOS or SHP2 reduces the exchange rate between GDP and GTP and reduces the GTP-bound RAS population. Mutated RAS proteins accumulate in the GTP-bound state. Many inhibitors have been developed to directly inhibit RAS, including covalent allele-specific inhibitors that bind to KRAS-G12C.