Fig. 1 |. Major types of TEs in mammalian genomes.
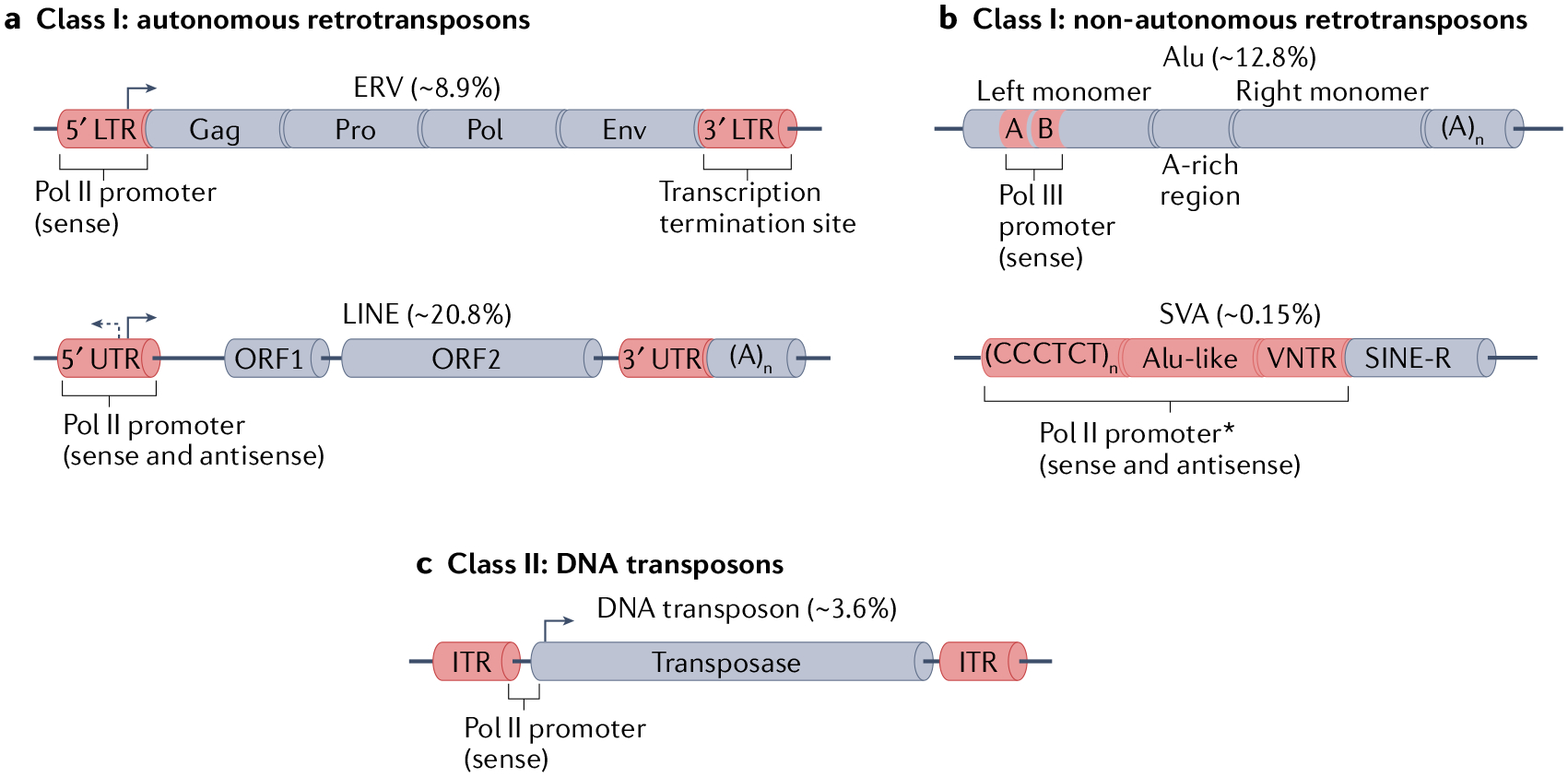
Transposable elements (TEs) are divided into Class I and Class II depending on their transposition mechanism1. Class I elements are called retrotransposons because they use RNA as an intermediate that is reverse transcribed into DNA and integrated in the genome (not shown). a | Autonomous retrotransposons encode all the required proteins for their retrotransposition. Endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) consist of two long terminal repeats (LTRs) flanking the open reading frames (ORFs) that encode the viral proteins. During evolution, ERVs are often reduced to a single LTR, or ‘solo LTR’, which renders them incapable of retrotransposition. Long interspersed nuclear elements (LINEs), such as L1, contain two ORFs that encode proteins required for their retrotransposition, which are flanked by untranslated regions (UTRs). At the 3′ end, they possess an adenines tail of variable length. b | Non-autonomous retrotransposons comprise those TEs that require the machinery encoded by autonomous retrotransposons to be mobilized (the TEs depicted here use the L1 machinery). Alu elements are primate-specific short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs), and their structure consists of two monomers derived from the 7SL non-coding RNA, flanking an adenine (A)-rich region. At the 3′ end, they possess an adenines tail of variable length. On the left monomer, boxes A and B indicate a bipartite promoter for RNA polymerase III (Pol III). SINE-VNTR-Alu (SVA) elements are hominoid-specific composite non-autonomous retrotransposons comprised of a 5′ region of a variable number of repeats of the hexamer CCCTCT, followed by an Alu-like region, a variable number of tandem repeats (VNTR), and a 3′ ‘SINE-R’ region derived from the LTR of human endogenous retrovirus K. c | Class II DNA transposons encode a transposase that is required for their excision and insertion through a ‘cut-and-paste’ mechanism. The transposase ORF is flanked by two inverted terminal repeats (ITRs). Asterisk indicates that the precise localization of the cis-regulatory feature within the delimited region is unknown. Numbers in brackets indicate the percentage of the human genome (chm13-v1.0 (REF.17)) comprised by the specific subfamily. env, envelope; pol, reverse-transcriptase; pro, protease.
