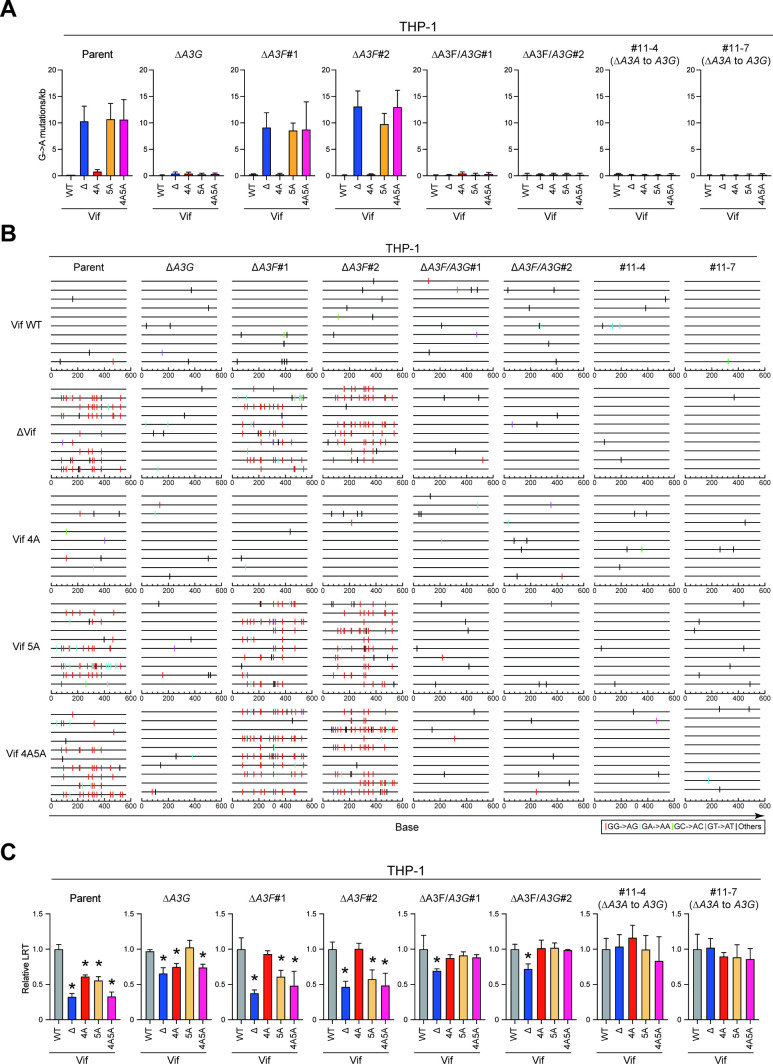
Fig 4.
A3 proteins inhibit Vif-deficient HIV-1 by both deaminase-dependent and -independent mechanisms in THP-1 cells. (A) G-to-A mutations. Average number of G-to-A mutations in the 564 bp pol gene after infection with hyper-Vif, hypo-Vif, IIIB Vif, or Vif-deficient HIV-1 produced from parental or A3-null THP-1 cells. Each bar depicts the average of three independent experiments with SD. (B) G-to-A mutation profile. Dinucleotide sequence contexts of G-to-A mutations in the 564 bp pol gene after infection with the indicated viruses produced from indicated cell lines. Each vertical line indicates the location of the dinucleotide sequence contexts described in the legend within the 564 bp amplicon (horizontal line). (C) Representative LRT quantification data for Vif-proficient, Vif-deficient, Vif4A, Vif5A, and Vif4A5A HIV-1 mutants produced from each A3-null THP-1 subclone. Data show LRT products of the indicated HIV-1 mutants produced in parental or indicated A3-null THP-1 cells. The amount of produced viruses used to infect SupT11 cells was normalized to p24 levels. LRT products were measured by qPCR. Each bar represents the average of four independent experiments with SD. LRT products were normalized to the quantity of the CCR5 gene relative to Vif-proficient HIV-1 (WT). Statistical significance was assessed using the two-sided paired t test. *P < 0.05 compared to Vif-proficient HIV-1 LRT products.