FIG 2.
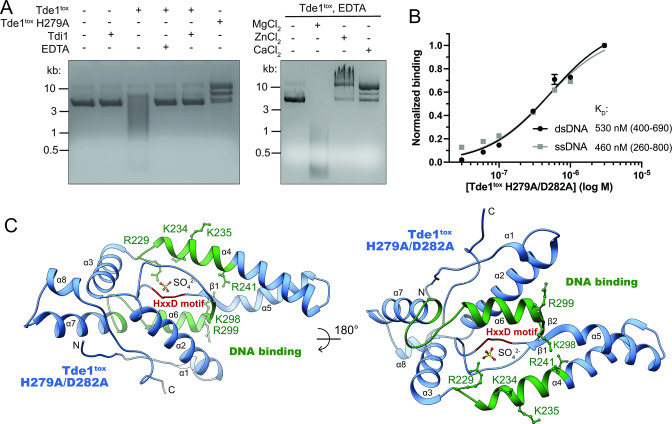
The DNAse Tde1 adopts an α-helical predominant fold with HxxD motif active site. (A) Refolded Tde1 Ntox15 domain degraded plasmid dsDNA. Nuclease activity was impaired by mutation of the HxxD motif, addition of molar excess immunity protein, or chelation of divalent cations with EDTA. Tde1tox nuclease activity impairment by EDTA was reversed by addition of molar excess magnesium, but not zinc or calcium. (B) Tde1tox with active site mutations interacted with both double- and single-stranded biotinylated oligonucleotides of random sequence, measured with biolayer interferometry. (C) A crystal structure of catalytically inactive Tde1tox H279A/D282A domain (Table S1) was obtained by molecular replacement using an AlphaFold2 prediction (36). Tde1tox adopts a single domain fold with the predicted DNA binding surface (green). Mutation of key basic residues (green sticks) to alanine or acidic residues decreased DNA binding affinity (Fig. S2F). The active site corresponds to the HxxD motif (red) and contains a modeled sulfate anion, present due to crystallization is high concentrations of ammonium sulfate.