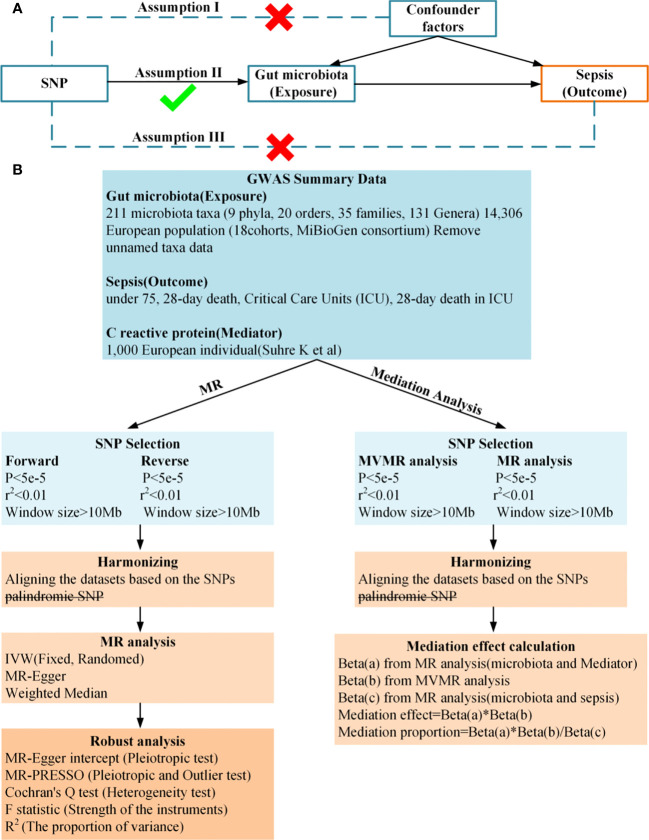
Figure 1.
(A), Principles of Mendelian Randomization: I) Independence: The genetic variants utilized in the analysis are not associated with any confounders that could potentially influence the relationship between the exposure and the outcome. II) Relevance: The genetic variants selected as instrumental variables have a strong association with the exposure. III) Exclusion Restriction: The genetic variants influence the outcome solely through their effect on the exposure, and not through any alternative pathways; (B), Flowchart of Bidirectional Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization and mediation Analysis.