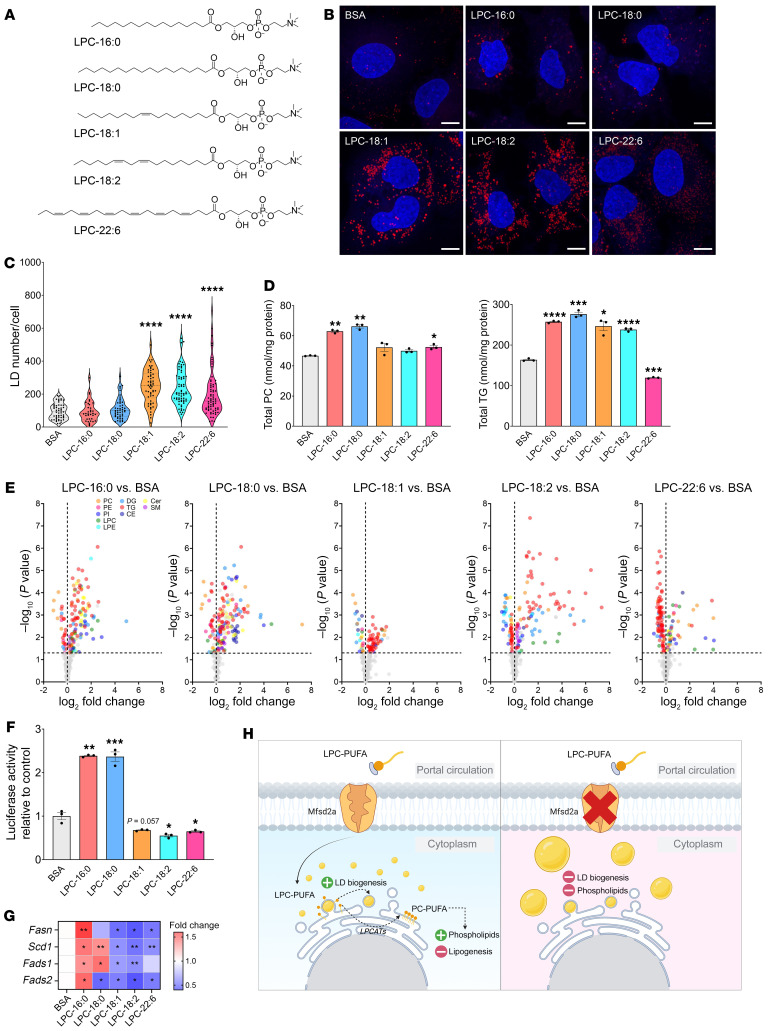
Figure 7. Unsaturated LPCs promote LD biogenesis and suppress lipogenesis in HuH-7 cells.
(A) Lipid structures of LPCs used in this experiment. (B) Confocal microscopy of Mfsd2a-GFP–expressing HuH-7 cells treated with the indicated LPCs or fatty acid–free BSA control. LDs were stained with LipidTOX. Scale bars: 10 μm. (C) Violin plot shows quantification of LDs per cell. ****P < 0.0001, 2-tailed Welch’s t test. Each dot in the graph represents the number of LDs in a single cell treated with respective LPCs. (D) Lipidomic analysis of Mfsd2a-GFP–expressing HuH-7 cells treated with the indicated LPCs or BSA control (n = 3 technical replicates per treatment). Graphs showing total PC and TGs. (E) Volcano plot showing the significantly changed lipid species in cells treated with respective LPC as compared with BSA control (colored dots represent significant species and are located above dashed line, indicating a threshold of P < 0.05). (F) pSynSRE-T-Luc luciferase activity of Mfsd2a-GFP–expressing HuH-7 cells treated with respective LPCs (n = 3 technical replicates per treatment). Graphs showing relative luciferase activity normalized to BSA control. (G) Heatmap showing qPCR analysis of genes involved in lipogenesis pathway. (H) Proposed model of this study. Data are represented as means ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001, 2-tailed Welch’s t test.