Fig. 3. Gap junctional communication (GJC) and 5-HT, but not K+ or H+ flux, are required for LR asymmetry in conjoined twins.
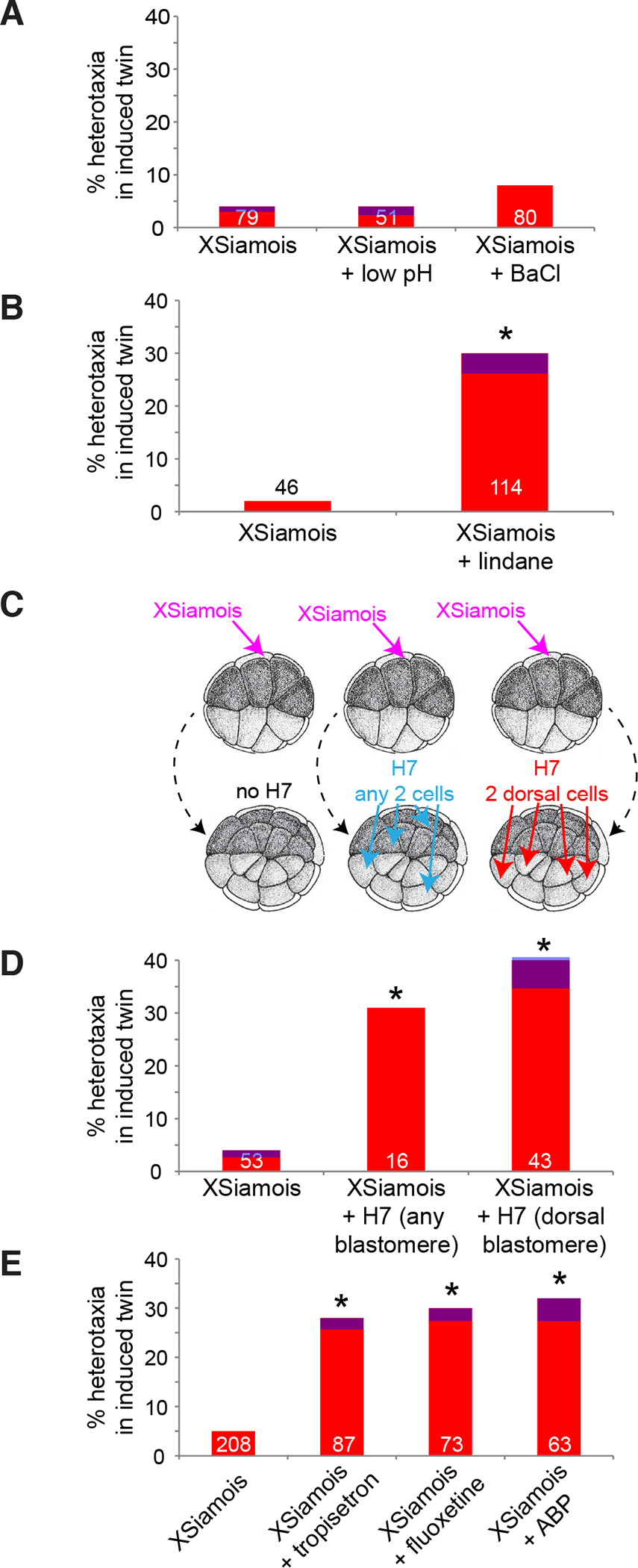
(A) Neither low pH, which inhibits H+ efflux pumps, nor BaCl, which blocks all K+ channels, disrupts LR patterning in late-induced twins when exposures start late. (B) Late treatment with lindane, which disrupts GJC, induces heterotaxia in conjoined twins. (C) A schematic detailing experiments with H7 mRNA, a dominant negative form of a chimeric connexin that disrupts GJC. All embryos were injected with XSiamois at the 8- or 16-cell stage. One set was injected with H7 into any two blastomeres in the top two tiers of the animal pole at the 32-cell stage. Another set was injected with H7 into any two dorsal blastomeres in the top two tiers of the animal pole at the 32-cell stage. (D) Disruption of GJC with H7 mRNA alters LR patterning in late-induced organizers, even when GJC is only disturbed in the dorsal cells; the dorsal cells contribute to the primary axis and not the induced twin. (E) Altered 5-HT signaling at late stages disrupts LR patterning in conjoined twins. In all panels, the numbers on the graphs indicate the sample size, *p<0.05 compared to untreated controls, Chi Square test. Red bars indicate inverted hearts, blue indicates inverted stomach and/or gall bladder, and purple indicates inverted heart plus stomach and/or gall bladder.
