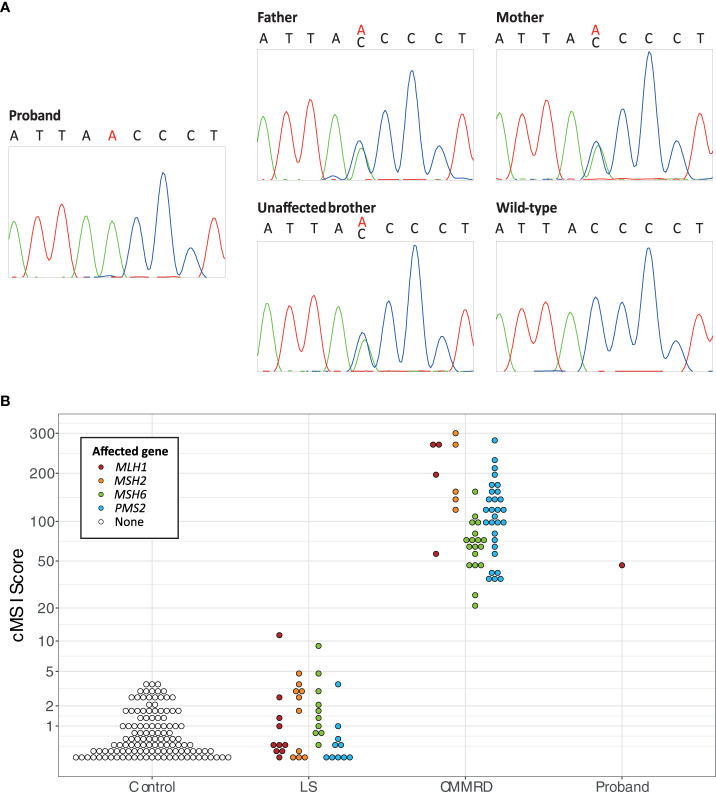
Figure 2.
(A) Sanger sequencing results of the segregation study of the MLH1 c.1918C>A variant, including a chromatogram of the proband showing the homozygous MLH1 c.1918C>A variant, chromatograms of the father, the mother, and the unaffected brother showing the heterozygous MLH1 c.1918C>A variant, and a chromatogram of the wild type sequence. (B) The constitutional MSI (cMSI) scores of 123 control, 40 Lynch syndrome (LS; MLH1 n = 10, MSH2 n = 10, MSH6 n = 10, PMS2 n = 10), 56 constitutional mismatch repair deficiency syndrome (CMMRD; MLH1 n = 4, MSH2 n = 5, MSH6 n = 18, PMS2 n = 29), and 43 control patients using data from Gallon et al. (4), compared to the cMSI score of the proband. The y-axis is scaled based on a logit transformation.