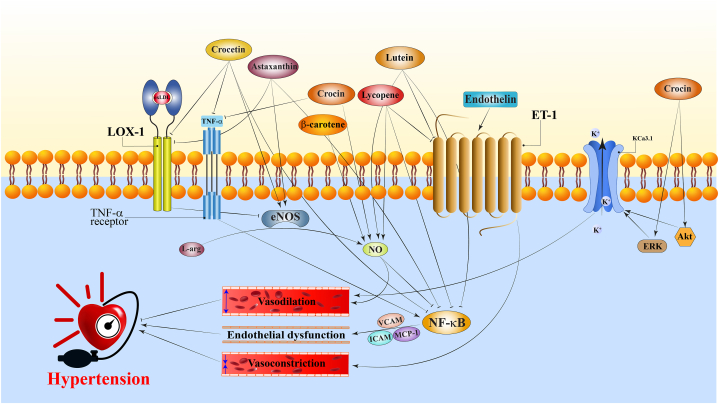
Fig. 2.
A schematic illustration of antihypertensive mechanisms of carotenoids. Carotenoids by inhibition of ROS, angiotensin II, and NF-κB induce antihypertensive effects. → present the promote/activate and ⊥ present the inhibitory/suppressive effects. CAT: catalase, eNOS: endothelial nitric oxide synthase, GR: glutathione reductase, GSH-Px: glutathione peroxidase, HO-1: heme oxygenase-1, L-arg: l-arginine, LOX-1: lectin-like ox-LDL receptor 1, NADPH oxidase: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxid, NF-κB: nuclear factor-κB, NO: nitric oxide, Nrf2: nuclear factor-erythroid 2-like 2, ox-LDL: oxidized low-density lipoprotein, ROS: reactive oxygen species, SOD: superoxide dismutase.