Figure 5. PRMT1 methylates ME2, inhibiting fumarate sensing.
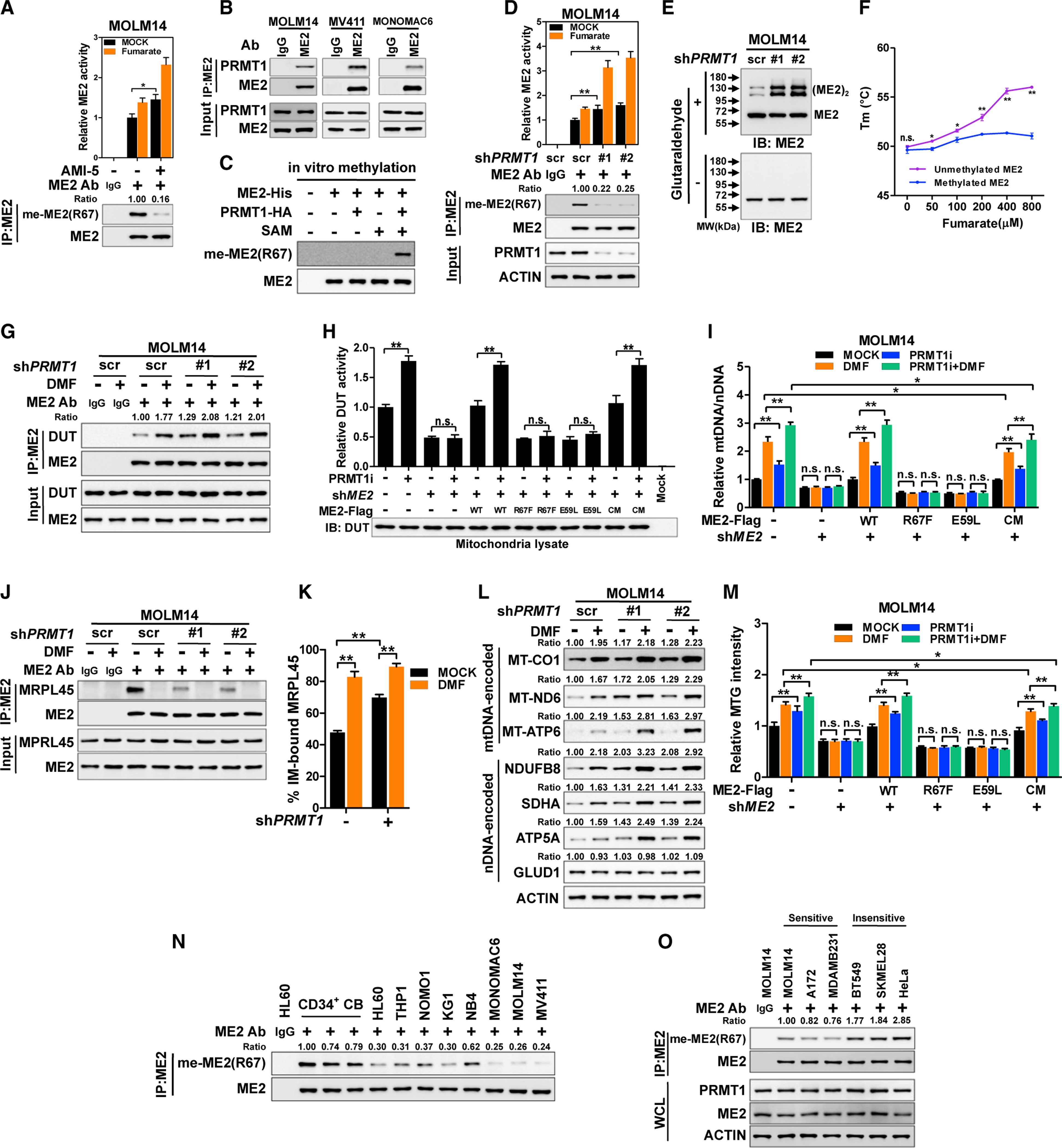
(A) R67 methylation of immunoprecipitated ME2 was determined in MOLM14 cells after AMI-5 treatment for 24 h.
(B) The interaction between ME2 and PRMT1 in AML cells was assayed.
(C) Recombinant ME2-His was incubated with PRMT1-HA in the presence of SAM. R67 methylation was determined.
(D and E) ME2 was immunopurified from control and PRMT1-knockdown MOLM14 cells, and subjected to western blotting and enzymatic activity assay (D).
Whole-cell lysate of MOLM14 cells was subjected to crosslinking assay (E).
(F) The melting temperature (Tm) of unmethylated and methylated ME2 (lanes 4 and 5 in C) was determined.
(G) Control and PRMT1-knockdown MOLM14 cells were treated with DMF. The interaction between ME2 and DUT was determined.
(H and I) ME2-knockdown and re-expression MOLM14 cells were treated with PRMT1i for 24 h. Mitochondrial lysate was subjected to DUT activity assay (H).
Stable cells were treated with PRMT1i and DMF as indicated. mtDNA was quantified (I).
(J–L) Control or PRMT1-knockdown cells were treated with DMF. Interaction of ME2 and MRPL45 was assayed (J). MRPL45 protein in inner-membrane and matrix fractions was quantified (K). The expression of mtDNA and nDNA-encoded proteins was determined (L).
(M) Stable MOLM14 cells were treated with PRMT1i and DMF as indicated. MTG intensity was determined.
(N and O) Endogenous ME2 was immunopurified from CD34+ CB cells, AML cells (N), and representative solid tumor cell lines (O) to determine R67 methylation.
Whole-cell lysate was used to detect PRMT1 and ME2 (O).
All data are presented as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; n.s. indicates not significant. See also Figure S5.
