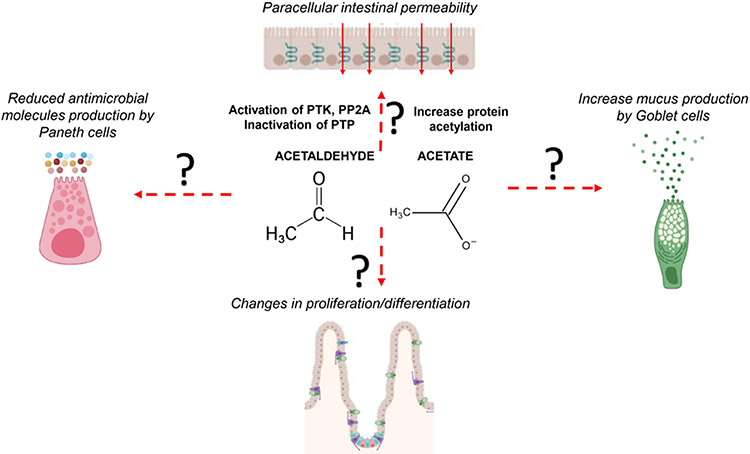
Figure 3.
Potential role of acetaldehyde and acetate in alcohol-associated epithelial pathogenesis. The mechanisms described for increased paracellular permeability are relative to studies conducted with Caco-2 cell lines. The in vivo impact of acetaldehyde and acetate on alcohol-induced epithelial dysfunctions in the different sites of the intestinal tract are not known. PP2A, protein phosphatase 2A; PTK, protein tyrosine kinase; PTP, protein tyrosine phosphatase.