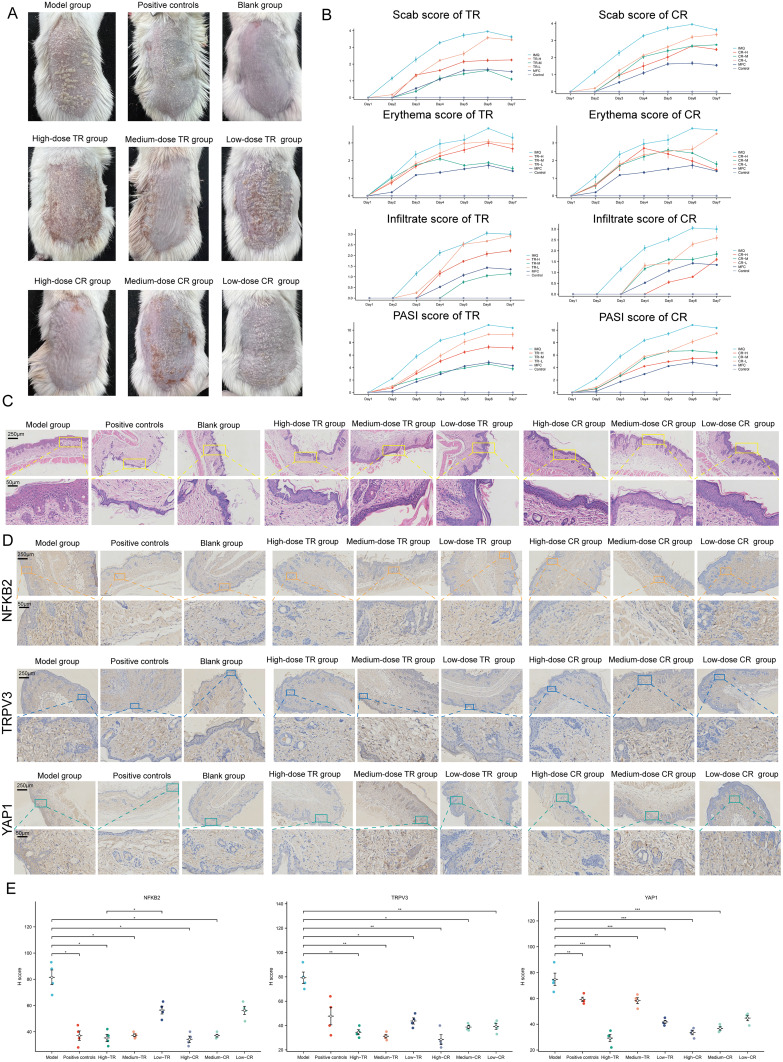
Figure 7.
Identification of the Mechanisms of Cinnamomi Ramulus (CR) and Tripterygii Radix (TR) in the Treatment of Psoriasis. (A) Representative photographs of the back of each group of mice. (B) Scab/Erythema/Infiltrate/psoriasis area severity index (PASI) score of each group for day1, day2, day3, day4, day4, day5, day6 and day7. Left: TR, Right: CR. (C) Skin lesions of each group were stained with HE (Magnification × 10, scale bars = 250 µm; Magnification × 40, scale bars = 50 µm). (D) Skin lesions of each group were stained with NFKB2, TRPV3, YAP1 (Magnification × 10, scale bars = 250 µm; Magnification × 40, scale bars = 50 µm). See also Figure S10. (E) Differences of NFKB2, TRPV3, YAP1 immunohistochemical staining intensity among nine groups as assessed by H-score (n = 4). One-way ANOVA was conducted. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Model, imiquimod; Low dose, 0.585 g/kg/day; medium dose, 1.17 g/kg/day; high dose, 2.34 g/kg/day. See also Figure S11.