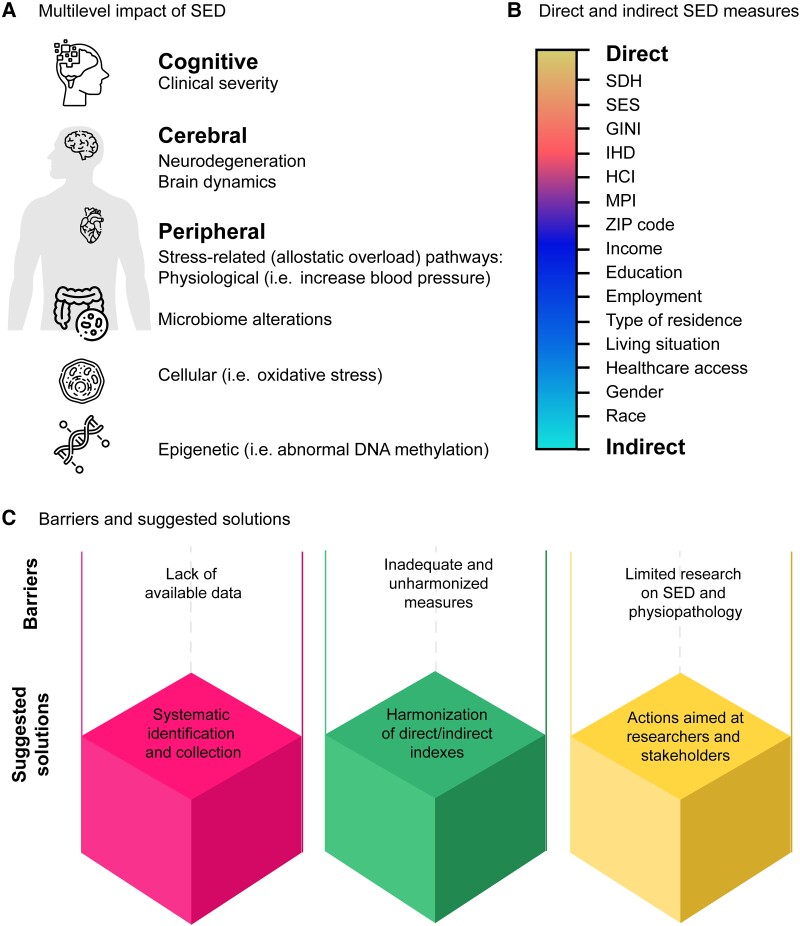
Figure 1.
SED and brain health. An overview of the multilevel impact of socioeconomic disparities (SED) on brain health. (A) Multilevel impact of SED and their effects on various aspects of brain health, including cognitive (clinical severity, daily-life functioning and cognitive dysfunction), cerebral (brain dynamics and neurodegeneration), and peripheral factors (inflammatory and immunological dysregulation, microbiome alterations, stress-related pathways, physiological dysregulations, cellular alterations and epigenetic modifications). (B) Direct and indirect measures of SED. Differentiation between direct and indirect measures of SED, with direct measures including social determinants of health (SDH) and socioeconomic status (SES), and indirect measures encompassing factors such as postcode (ZIP code), income, education, race, gender, employment, type of residence, living situation and healthcare access. (C) Barriers and suggested solutions. Identification of barriers and suggested solutions for addressing challenges in future research aimed at developing equitable global approaches to brain health that consider the impact of SED. HCI = human capital index; IHD = index of human development; MPI = multidimensional poverty measures.