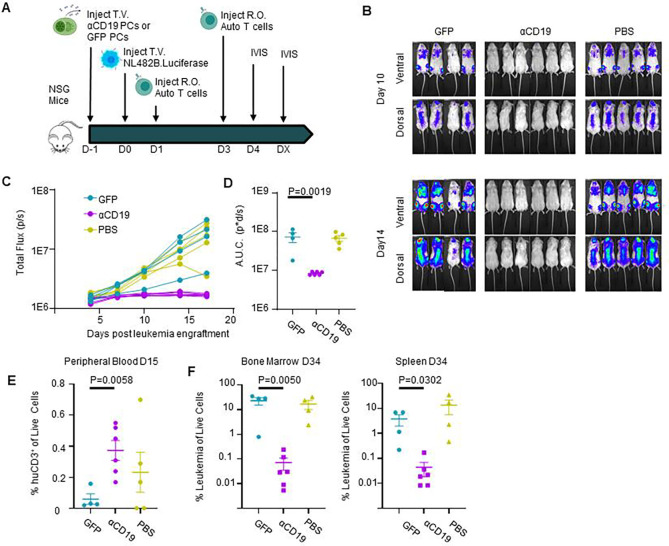
Figure 5: CD19KO PCs engineered to secrete αCD19 bispecific can prevent leukemia engraftment.
A) Schematic showing prophylactic treatment of a patient-derived xenograft model of high-risk ALL. Either GFP.CD19KO or αCD19.GFP.CD19KO ePCs were injected intravenously into immunodeficient NSG mice. 24 hours later, luciferase-labeled patient-derived NL482B [Children’s Oncology Group unique specimen identifier PALJDL] cells were administered. Finally, we delivered T cells syngeneic to the ePCs in two doses by retro-orbital injection. B) Bioluminescent images showing dissemination of the luciferase-expressing leukemia cells (color scale; min:8×103 max:1×105). C) Leukemia growth was quantified via total bioluminescent flux at the indicated time points. D) Area under the curve analysis was conducted with baseline correction 1×106 flux. E) Peripheral blood flow analysis showing the percent of CD3+ cells of singlet live cells is elevated in the αCD19 cohort. Mice were euthanized 34 days after leukemia engraftment and tissues were stained and analyzed by flow. F) The percent CD19+ of live CD45+ singlet cells shows suppression of leukemic cells in bone and spleens of the αCD19 ePC cohort. A-D) Data from one donor with p-values calculated by one-way unpaired ANOVA with Šídák’s posttest (D) and unpaired student’s T tests between GFP and αCD19 cohorts (E-F). Illustrations created in part with biorender.com.