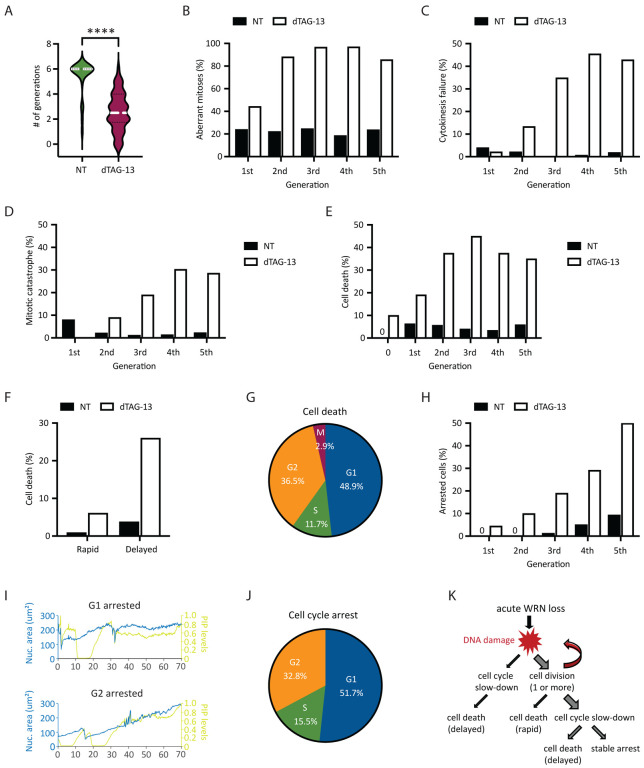
Fig 4. Heterogeneity in the fate of WRN-degraded MSI-H cancer cells.
RKO reporter cells were treated or not with 0.5 μM dTAG-13 and imaged by time-lapse microscopy over a span of 6 days. Manual tracking was performed on 25 vehicle-treated and 50 dTAG-treated cells. (A) Cell division activities. Most of vehicle-treated cells divided at least 6 times, producing 840 tracked progeny. By contrast, dTAG-treated cells divided less frequently (average 2–3 times, range 0–6) and produced less progeny (377 tracked). (B) Mitotic abnormalities as a function of cell division. A mitosis was scored as abnormal if it exhibited one or more of the following features: bridging, micronuclei formation, cytokinesis failure and/or mitotic catastrophe. (C) Frequency of cytokinesis failure as a function of cell division. (D) Frequency of mitotic catastrophe as a function of cell division. Mitotic catastrophe was defined as any mitosis that resulted in complete failure to divide (failed mitosis), multipolar chromosome segregation or rapid induction of mitotic cell death. (E) Frequency of cell death as a function of cell division. Note that 10% of dTAG-treated cells died without undergoing a single mitosis (denoted as generation 0). (F) Cell death as a function of time. A death event is defined as rapid if it occurred <10 h after the latest mitosis from which the cell was born. Otherwise, it is defined as delayed. (G) Cell death as a function of cell cycle position. (H) Frequency of cell cycle arrest as a function of cell division. (I) Example traces of two dTAG-treated cells showing arrest in G1 (upper panel) or G2 (lower panel). (J) Cell cycle arrest as a function of cell cycle position. One of two independent experiments is shown. (K) Diagram depicting the various observed fates of RKO cells following acute WRN degradation.