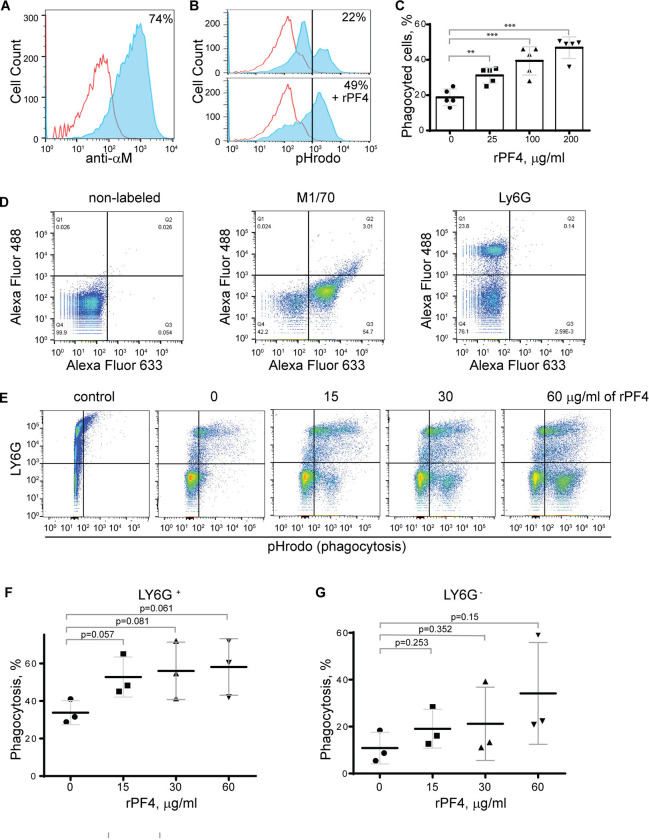
Figure 4. Effect of rPF4 on phagocytosis of S. aureus bioparticles by differentiated neutrophil-like HL-60 cells, peritoneal neutrophils, and monocyte/macrophages.
(A) HL-60 cells were differentiated into granulocytes by incubating in the presence of DMSO, and expression of Mac-1 was determined by flow cytometry using anti-Mac-1 mAb 44a followed by Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated secondary antibody. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of bacteria uptake by differentiated HL-60 cells. pHrodo red-labeled S. aureus bioparticles (100 μg/ml) were preincubated without or with rPF4 (200 μg/ml) for 1 h and added to HL-60 cells. Phagocytosis was determined by flow cytometry after 1 h at 37 °C. Shown are representative histograms (from five individual experiments) in the absence and presence of rPF4, and numbers indicate a percentage of pHrodo-positive cells. (C) Effect of different concentrations of rPF4 (25–200 μg/ml) on phagocytosis of S. aureus bioparticles by HL-60 cells. The percentage of pHrodo-positive cells was determined by flow cytometry after 1-hour of incubation with S. aureus bioparticles. Values are mean ± S.D. from 5 separate experiments. **p≤ 0.01, ***p≤ 0.001. (D) The identification of mouse neutrophils and macrophages in peritoneum lavage 4 h after TG injection. Peritoneal cells were incubated with anti-Ly6G mAb (neutrophil marker) and anti-Mac-1 mAb M1/70 (neutrophil and macrophage marker). Shown are the total population of gated cells (left panel), cells expressing the M1/70 epitope (central panel), and cells expressing the Ly6G epitope (right panel). (E) Phagocytosis by Ly6G+, CD11b+ neutrophils and Ly6G−, CD11b+ monocyte/macrophages of pHrodo-labeled S. aureus bioparticles (nontreated (0) and treated with different concentrations of rPF4). Control, non-labeled cells. A representative of three separate experiments is shown. (F, G) Dose-dependent phagocytosis by neutrophils (Ly6G+) and macrophages (Ly6G−). Values are mean ± S.D. from three experiments; The differences in phagocytosis in the absence and presence of rPF4 are not statistically significant.