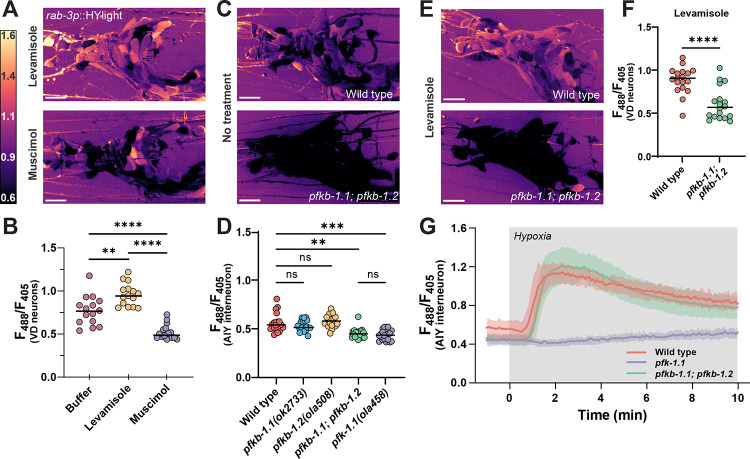
Figure 3: Neurons depend on PFKFB enzymes to modulate rates of glycolysis.
(A) HYlight ratio of 488/405 nm excitation in the nerve ring of worms mounted in 10 mM levamisole (top) or 50 mM muscimol (bottom). Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Quantification of HYlight ratios in the VD neurons when worms are mounted in either M9 buffer, 10 mM levamisole, or 50 mM muscimol. Significance represents P-values of 0.0013 (**) or <0.0001 (****), as calculated by ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc test, for 15 animals. (C) HYlight ratios in the nerve ring of wild type (top) or pfkb-1.1(ok2733); pfkb-1.2(ola508) double mutants (bottom) mounted in M9 buffer. Single mutant images and quantification in Figure S3. (D) Quantification of HYlight responses for indicated genotypes in the AIY interneuron. Significance represents P-values of 0.512 (WT vs. pfkb-1.1), >0.999 (WT vs. pfkb-1.2), 0.927 (WT vs. pfkb-1.1; pfkb-1.2), or <0.0001 (**), as calculated with ANOVA/Tukey post-hoc test across 18 animals. (E) HYlight ratio in the nerve ring of wild-type and pfkb-1.1(ok2733); pfkb-1.2(ola508) double mutant animals exposed to 10 mM levamisole. (F) HYlight ratios quantified for indicated genotypes in VD motor neurons in the presence of 10 mM levamisole. P-value of <0.0001 (****) is shown as calculated by unpaired t-test across 18 animals. (G) HYlight responses in the AIY interneuron for the indicated genotypes under transient hypoxia. The pfk-1.1(ola458) mutant animals do not increase upon hypoxia, whereas pfkb-1.1(ok2733); pfkb-1.2(ola508) double mutant animals, which start at a similar mean ratio as shown in (D), display responses to transient hypoxia that are indistinguishable from wild type. Shading represents the standard deviation around mean values for 18 worms per treatment. Hypoxia treatment represented by grey box.