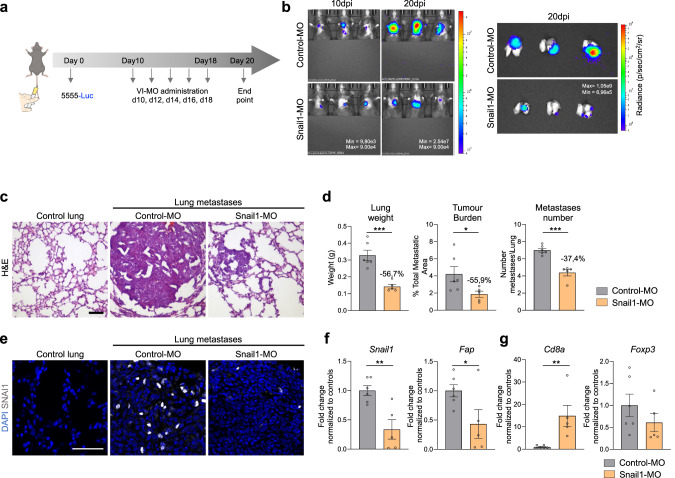
Fig. 6. Snail1 systemic targeting significantly reduces melanoma lung metastases in mice.
a Scheme of the experimental approach. Nine days after tail vein injection of BrafV600E-5555 cells, C57BL/6 mice were injected with vivo-morpholino (VI-MO) control (Control-MO) or Snail1 morpholino (Snail1-MO) every other day. Created with BioRender.com. b Bioluminescent signal in mice and lungs from (a). The BLI scale is represented in each panel. Units: p/s/cm2/sr. c Representative H&E-stained lung sections after VI-MO treatment. Scale: 100 µm. d Final lung weight, tumour burden and number of metastases from mice in (a) were quantified at the end of the experiment. e Representative images of immunolabelling for SNAI1 in lung sections after VI-MOs treatment. Scale bar: 50 µm. f, g Snail1, Fap, Cd8a and Foxp3 mRNA expression assessed by RT-qPCR lung metastases from mice treated with Snail1-MO (n = 6 Control-MO and n = 5 Snail1-MO). Data are normalised to samples treated with Control-MO. Data are represented by Mean ± SEM and statistically significant differences are tested by unpaired two-tailed Student t-test. Each dot represents one animal (ns = not significant, * = p < 0.05, ** = p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).